World History- Ancient Greece
Greeks were once Paleolithic and Neolithic too- started farming around 3200 BCE
Mycenaeans
1st well organized society in Greece (about 100 years after Hammurabi’s code)
spoke an Indo-European language
The Iliad, The Odyssey both were written about the Mycenaeans ^^
Minoans
Society located South of the Mycenaeans
very similar to the Mycenaeans (the Mycenaeans would pull a lot of their culture form the Minoans)
Centralized Kingdom » under one rule
Linked to Mycenaeans via trade, politics, culture, intermarriage
Based in trade » thrives in trading + economics
Writing developed for record keeping
Their records suggest government involvement in trade
Would eventually be conquered by the Mycenaeans
«Mycenaean Society would collapse around 1200 BCE»
Greek Dark Ages: goes from large kingdom to more tribal set up » would be decentralized for the next 500 Years
Greek City States- (similar but different from the ones of Mesopotamia)
The original tribes will grow to be independent City States called The Polis
Nature of the Polis:
there was a focus on community- everyone has an important role
Self Identity is very tied to your Polis- you are your Polis
Acropolis- the center of the Polis with many religious buildings
There is no political unity but saw themselves as under that culture with outsiders being Barbarians
Different Poleis had different systems of Government including:
Monarchy
Oligarchy
Aristocracy
Democracy (Athens)
Even with these few generalized government systems every Polis government is different
Greeks thought of Democracy as an ineffective way of government » thought it was only suited for smaller city-states
Geographic Influence on Greece:
farming took much longer for the Greeks to discover and develop because of Greece’s rocky mountain terrain
created poor farming
this leads to the creation of a maritime culture leading to trade being essential » they become excellent merchants
poor communication
difficult rivers to navigate
City States become Isolated
Limited Farming
this created very bound/ close families depending on each other for survival
Geography causes a lack of Political Unity but excellent sailors and merchants
Greek Colonization - they spread out largely over the Mediterranean (wherever they could sail to)
did so for the sake of trade»
did so for exilement
»Trade»
They did not have great agriculture but what they did grow was highly in demand:
Olives> oil
Grapes> wine
Because of trade- social status is not based on landownership leading to a small but powerful middle class that will start growing larger
The Greeks would learn from other Cultures also…
The Phoenicians
Known for their alphabet based on phonics
The Greeks would adopt this alphabet of phonics which would be revolutionary for the culture- much easier to learn»
»Social Effects of the Alphabet»
There were no “Scribes” because now anyone can learn to read now- not everyone did know but now it was much easier to
Literacy and numbers becomes essential for trade across the sea
The Middle Class would start to perpetuate their status through education- allows their children to keep that class or move up
This leads to an educated society
Middle class will play a huge role in democracy- middle class will demand a political seat and be denied by the wealthy » conflict leads to democracy» Athens
»Athens»
Athens did not start out as a democracy- originally an aristocracy
Athens is unique because it had a smaller (but growing) middle class that would feel the pressure of the cities trying to get land.
Upper class will push middle class down trying to gain as much wealth through trade
Middle Class land owners having to sell themselves to slavery to pay off debts
Central Figure: Draco
An elite that felt the worry of the angered middle class» leads to the Draconian Legal Code
Excessively difficult and cruel punishments
Favored the elites but everyone was under the law
does not solve the crisis of those sliding into slavery
somewhat diminishes the class differences
now because of the code and debt people were frequently sent away (exiled)
Central Figure: Solon (comparatively opposite to Draco)
Solon was an elite that felt sympathy for the middle class- reformer
He publicly recited poems that prompted some sympathy for the poor by the elites
Solon would go on to:
free those enslaved
abolish slavery stemming from debt
brings back those that are exiled
allows commoners into government
“everyone” could now vote on laws and discuss them» revolutionary because now change could come through democracy without a revolution, conspiracy or violence
Athens will face pressure from limited resources and this will lead to colonization
Greek Wartime Innovations
Sense of community in the Polis leads to fighting FOR the Polis and defending the Polis ~Polis is love, Polis is life 😍~
Greek would get very good at Calvary (soldiers fighting on horseback)
Greeks will become innovators in warfare due to competition over resources:
Greek Phalanx- based on training and discipline» intimidating to enemies ~jumpscarrrree~
Diminishes the individual to emphasize the greater whole of the Polis
Greek Hoplite- heavily armored soldier that was very well trained, equipped with a spear, and many weapons and backed by infantry
this would be very effective
Spartan Militarism
Militaristic Society- best, most brilliant warriors of Greece
Similar pressures as the athenians- limited food, and fast growing population- conquers and enslaves the Helots to gain resources and force them in slavery
Helots are constantly rebellious and hate the spartans-
Spartans are consistently worried that any day there will be an uprising and the helots will kill them
spartans had to become very good warriors because constant fighting and worrying over the helots
Started out as a monarchy with a aristocracy
Sparta middle class (men) will eventually gain political rights after threatening to let the helots riot and rebel- commoners are the spartan military- (feel the upper class owes them something for keeping the wealthy from experiencing the wrath of the Helots )
Started out as a monarchy and developed to 2 kings were part military leaders that would be elected by the people- had advisors/ counselors around them
Spartans were expected to set aside desires, individual wants and needs aside for the good of the city
“better to be dead than to surrender”
revered by other greeks for being the best warrior society
Men were gone training for fighting a lot of the time- almost absolutely no men
this leads to women managing the estates and giving order to the helots
women could own their own property
women could move about freely with very little control over their lives (sorta??)
Greeks in Asia Minor
Persian Wars
Persians want to control the trade of Greece up to the black sea to Ukraine- VERY desirable resources (breadbaskets)
Persian army had conquered almost all of asian minor- including some greeks
despite Persians being very convincing, the conquered greeks were very unhappy under their rule and described the Persians as barbaric
When the Greeks finally revolt against the Persians the Athenians want to help
Ruler Darius wants to crush the revolt and rule over Greece
very confident in his army, couldn’t even imaging losing to Greece- lost anyway (LOSER 😛 )
His son Darius would invade Athens
Athenians would be able to decide the fight of the battle- major advantage that lets them set traps»
Forced Persians to cross swamp land- renders horses useless and athenians won^^
leaves Persians bitter and wanting revenge
Darius’s son Xerxes would then continue the fight ^
Greeks aren’t naive so Athenians inform the other city states that they need to unify to form a strong alliance against the Persians»
Formation of the Delian League- Main Goals:
protect Greece from the Persians
Liberate the greeks from Persian control
Pericles of Athens will be the main leader- uses the league to build up the Athenian Wealth
this creates resentment from the other city states though because now athenians are so much more powerful and wealthy and other city states are worried athenians will subjugate them under their rule
Spartans are also angry at Athenians and refuse to ever submit under their rule
Persians will eventually lose war
Athenians want to keep the league but the other city states become angry because they don’t want to be under Athenian rule
as a result, Athens and Sparta will go to war- both find allies and rip Greece apart by side picking» Peloponnesian War
Spartans encourage revolt and eventually claim victory but the region is exhausted and trade has ground to a halt
This tragedy will lead to reflection and the creation of great art
Greek Philosophy
Art, dramas, philosophy, literature
Socrates (470-399 BCE)
Urged self reflection- “Know thyself”
“the unexamined life is not worth living”
no virtue in doing things because of tradition and being told to do things
Knowledge is virtue- knowing thyself is the basis of all knowledge
was previously exiled from Greece for a long while
teaches through a series of dialogues and ethical questions with no predetermined answers- Socratirial Method
may not know facts but an educated person will know themselves
Plato (427-347 BCE)- student of Socrates that wrote everything down for him
An idealist
wants to understand the nature of reality and what reality is
“what is real?” Concerned with the nature of truth
Believe there is two worlds: 1) one where we observe the world through our own lens- Our reality- human flaws and human frails 2) other world that is perfect and reflects a true unchanging reality- the perfect ideal of the world with nothing is wrong; the ultimate reality
This world is a distortion of a perfect world
the flaws of the world reflects our flaws and out there is a realm with the ideal world
Example of this ideology: a chair in our world is “not a real chair but rather an imperfect derivative of the ideal chair with no flaws”
Lays out an ideal republic- why model a government based off flawed government?- don’t study imperfect models, study the perfect ideal
Platos allegory of the cave: we are all the prisoners held captive by our own reality and only seeing imperfect reflections of what is real
Only by becoming enlightened (by mediating on the ideal) can we see the world for what it really is and see true reality
Aristotle (384-322 BCE)- student of plato
More interested in the observable, measurable reality
believes knowledge comes from analyzing the real world
collecting and learning more facts leads to real knowledge (much of the scientific method comes from him)
don’t just study abstract method- the answer lies in the nature of the real world
Poet, philosopher, scientists chemist
analyzes and separates the different forms of government that different greek city states
believes the planet is composed of 5 elements (fire, earth, water, air, and ether (stuff the universe is made up of)
Earth is at the center of the universe and everything orbits it
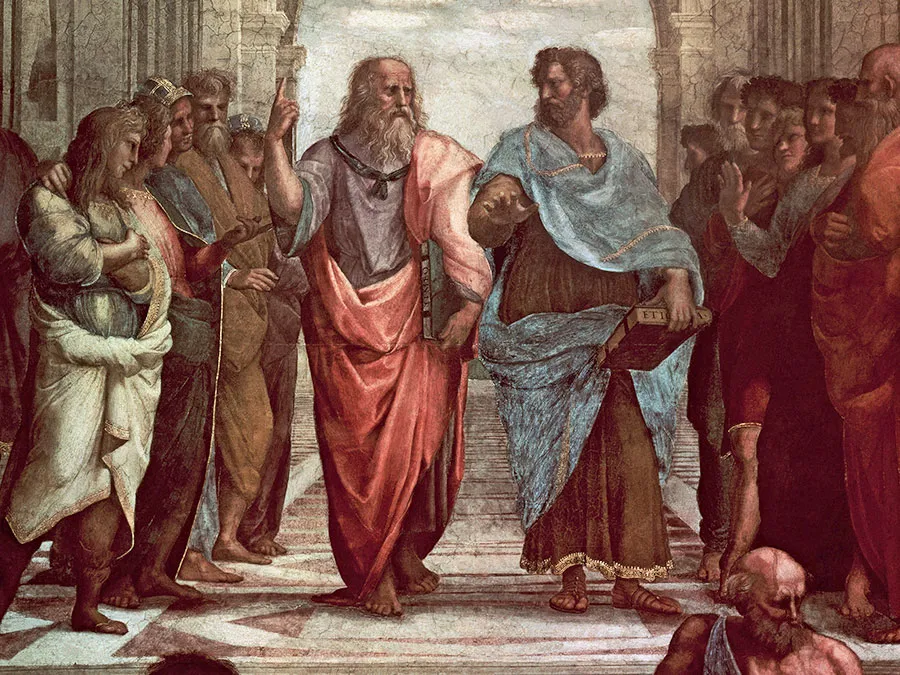
Closely examining the photo gives good representation of the beliefs of Aristotle (right) and Plato (left)

Hellenistic Society
Bigger and like the greeks but not greek
Alexander the Great- conquers the known world by the age of 32
mystique, charm, romanticized
greek became the common language of the land he conquered- conquered all the way to some parts of India
influence will be mainly cultural
personal tutor was Aristotle but he’s still not Greek
Rise of Macedon
Macedon is cultural cousins to greek
Philip II of Macedon was ruler of Macedon and father of Alexander the great
Unhappy with the Peloponnesian war between the Athenians and the Spartans because of effects on trade
Plans to conquer and invade Greece since the Persians could not
uses the lack of the Delian league and lack of unity to politically conquer Greece- strategically severs any alliances and takes advantage of distrust
Got the greeks to buy into his rule by going to war with Persians to liberate the Greeks under the Persian rule- is promptly assassinated
Alexander the Great would be responsible for eliminating any threat (other people) to his chance of taking the thrown
Once king he will be responsible for liberating the Ionians (greeks under Persian rule)
Worshipped Egyptian gods to show respect- he’s polytheistic so what’s a few more gods 🤷♀
Crossed the Indus river valley and conquered the rest of the known world
partying and drinking would eventually kill him
there could be no empire without him and there would be a 40 year civil war among his generals over who would rule
Alexander’s kingdom would them be divided into 3 political units- still a Hellenistic kingdom
no political unity but culturally unity and trade
Leadership and elites speak greek- basically if they were important they would speak greek »
Trade will be based on greek culture
Hellenistic society was extremely cosmopolitan (knowledgeable of the world around them)
Hellenistic society was very multicultural (culturally hellenistic but must embrace diversity to maintain power)
» With a majority of people speaking greek, trade and spreading of science and culture would be unified and happen much more easily»
“Hellen” = greek “istic”= like } Greek like but still Macedonian- blending of cultures
Alexander the great known for establishing cities~ One way different cultures would be Hellenized
Once Alexander died, the government officials would continue the tradition of colonization spreading greek culture VERY far (some statues of Buddha look like Alexander)
Spread of roads, bridges, and harbors for trade- greek infrastructure spreading
»Emphasis on NO political unity but very much CULTURAL and ECONOMIC unity (cant emphasize this enough apparently)
» With a majority of people speaking greek, trade and spreading of science and culture would be unified and happen much more easily»
City of Alexandria
Library of Alexandria- burns to the effing ground apparently
Common language would lead to the spread of science and further development of different philosophies
Epicureanism- for that time period, it is a philosophy that says the meaning of life lies in seeking pleasures (not just of the flesh but also the avoidance of pain)- do so by ignoring politics, looking into your own feelings (escapism philosophy), letting go of what causes them pain or discomfort
Stoicism- believed that personal achievements don’t matter and the meaning to live is to live a very virtuous life;
accept and endure the bad parts of life; first to articulate the brotherhood of life-”we are all in this together”;
first to articulate the idea of Natural Law: There are natural laws in the universe that dictate how life happens on earth- if you understand the natural laws you can better understand the world and how to live in it
All humans are kin; we need to learn to live in harmony with one another and endure the rough patches in life
Key Figure: Zeno (335-262 BCE)
Hellenistic Scientists
Aristarchus (310-230 BCE): Astronomer; figured out the reasoning of why mercury looked like it was going backwards: the sun was the center of the solar system and everything orbited around it
Euclid (300BCE): Mathematician- studied Geometry; worked in the library of Alexandria; we
Archimedes (287-212 BCE): soldier and inventor and mathematician; invented the compound pully to lift weights; the archimedes screw; articulated the principle of water displacement is equal to the weight of the solid object displacing it
Roman Empire
Nobody:
Romans:
Etruscans
Hail form northern Italy
Would encounter and trade with the greeks- strong dose of greek culture now
They are nomadic and will eventually settle on the edge of the Tiber River
previously occupied by the Latins which will be conquered by the Etruscans
elites will be Etruscans and commoners will be Latins
Will have a lot of trade with greeks- will adopt the greek alphabet and adapt it to the Latin alphabet of the 26 letters
»Not a lot of solid information about this time period- a lot of “information” is based in mythology- we do know there was a king that would be other thrown and the Roman Republic would start»
Roman Republic
had a larger population and spread out more- therefore would not have democratic features
Assemblies to elect leader but the power was very tipped towards the elites and wealthy
Patricians- wealthy land owners and military leaders- would make up the Senate
the senate was an aristocratic system that had the power of the purse
The Consuls- an executive office; had executive power; was elected by the senate, senate attempted to act as advisors to the consuls
Rome would be a society based on the law and nobody was above the law- all people and all societies should be under the same law
Rome made firm distinctions between civil disputes and criminal disputes
Roman law would try to find a fair solution for all parties involved in disputes
Roman law will be rooted in logic rather than tradition
Struggle of the Order
Plebeians- anybody that wasn’t enslaved but wasn’t wealthy or elite- does not like the Patricians
wants a far equal voice in government
leads to tension and fight from the Plebeians- would later go on strike to make a point
Big problem for the Patricians because plebeians are the backbone of society
Patricians would allow them to express grievances grievances in court
Plebeians would battle for a more fair written law leading to everyone knowing their rights and the law
Can argue cases before the court
Equal before the law around 280BCE
Written Law» the Twelve Tables
Roman Expansion
would adopt and adapt the greek gods as their Roman gods (ie Jupiter, Mars…)
would build stone bridges and roads to incorporate Italian peninsula
Dispute with plebeians» Citizenship matters- romans would grant citizenship to those outside of Rome
Citizenship would soon become a symbol of status» some would even voluntarily enslave themselves to work for a few years to later be set free and become a citizen
However: Rome would not make citizenship universal- they viewed it as a privilege not a right (would take it away if they feel it deserved)
Will expand for the sake of needing more resources to feed growing cities
Origins of Imperialism
any external threat to the Roman power would be seen as an existential threat- “we need to destroy them before they destroy us”
that threat would become the Carthaginians - great tension and competition
Carthaginians would be ethnically Phoenician
More than romans, Carthage would feel the demographic pressure due to being strictly maritime and in need of resources from the North (where the Romans were) (South was not an option as that was where the Egyptian desert was)
these tensions and need fore resources leads to the Punic wars
Punic Wars (264-133 BCE)-Series of long drawn out wars between Carthage and Rome
Romans would build up their navy and take Sicily from the Carthaginians
Would set up Provinces in captured territories leading to a weakening of the institution (first province was Sicily)
Hannibal- leader of Carthage during the wars that led the march into southern Italy (on elephants :0 )
Rome would march in behind them to retake Spain and cut off their supplies; would then move on Carthage and cause Hannibal to leave Italy to defend the city
Results and Effects of the Punic Wars
Rome would win and be able to feed itself- first step to becoming an empire :0
Spoils of war were plentiful- got amazing wealth, gold, and enslaved people
Aqueducts would be a new invention along with new public facilities (bath houses, gymnasiums, libraries, etc)
Territory would be divided up into Latifundas
Massive Plantations run by Patricians and worked by enslaved people
these Latifundas put Plebeian farmers into a tight spot since they would be undercut by Patrician farms and since they would have to repair their land after being gone in war for years- would end up having to sell their land to the Patricians and moving to Rome
creates a growing poor population in Rome and lots of disorder
Leads to the creation of more public works like circuses to try and keep a lid on the chaos as veterans flood into the city (cuz that will fix it 😃 👍)
Tiberius Gracchus
elected consul member who would call for land reform to limit the size of these Latifunda and redistribute the rest of this land to the poor to get them out of the city
would be murdered by angry Patricians (RIP 💀 )
His brother Gaius Gracchus who would also try to bring reform would be murdered too
There is severe tension because these war veterans are getting no more than bread
The Romans government is not adapting - leads to a civil war
Roman Civil War
Because communication was so hard in this civil war the “guard rails” would be taken off generals so they could do what they needed to do (or what they wanted to do (AKA conquer Rome)) (seriously who thought that was a good idea??)
Sulla (138-78 BCE)
Set himself up as a dictator in Rome for about 9 years
tried to reform the system and reestablish the republic but would not really be successful
Pattern of conquering hero takes Rome, rules, and it repeats
looking more and more like an empire with imperialism
Pompey (106- 48 BCE)
would conquer all of modern Spain
allied himself with Julius Caesar- would eventually have a falling out and kick Caesar out
Julius Caesar (100-44 BCE)
Conquered modern day France (Ghall)
Would start to campaign and later assassinate Pompey
Bring back Cleopatra (69-30 BCE) after his campaign looking for Pompey
tried to use his power to help the Plebeians and restore stability (rules for 1 year)
colonized areas in Africa
abused his power
Brutus (85-42)
was pardoned by Caesar and thought of by Caesar as a little brother
was close with Caesar however thought he was Dangerous leading to him joining the conspirators and aiding in the Assassination of Julies Caesar (44 BCE)
now there is a power grab as all stability is thrown out the effing window
Mark Anthony and Augustus (Octavian) would fight for the control of Rome
Octavian is based out in the west (campaigns for Italian Nationalism)
Mark Anthony will marry Cleopatra and control Egypt and Greece (campaigns himself as a liberator of Greece and Egypt)
Mark Anthony and Cleopatra will have a Romeo and Juliet moment leading to the victory of Octavius and the death of the Republic
Imperialism society will emerge
Pax Romana- “The Roman Peace”
“The glory days of Rome”- the Hellenized empire
Greco-Roman empire

Rise of Christianity
Jesus of Nazareth (4 BCE- 33 CE) Context
Jesus was born in the land of Judea which had a lot of conflict with Rome- current king was Tiberius
Judea and Rome
Very violent times- Judea and Rome would not get along- religious tensions because the hebrews would reject Roman gods
Romans did not comprehend the idea of monotheism; lot of cultural misunderstandings
additionally there was a revolt in Judea of Roman culture
Hebrews found the Romans were greedy and violent
Romans saw Judea as a constant problem so they positioned a permanent army there and made the people of Judea pay higher taxes as a result
Sanhedrin
Jewish Elites put in charge by the Romans to handle the public and collect taxes
Zealots
political groups that wanted to force the romans out of Judea and would conduct political assassinations of roman officers
Messiah
John the Baptist would prophetically announce the Messiah was close at hand- people were expecting a political, military general not a preacher
Hellenistic Mystery Cults
secret religious groups in the Greco-Roman world
it is believed that these groups had an influence in the writing of scripture
Cult of Dionysus
lots of parallelism of the Father and Son telling of Christianity in the story of Dionysus
also partook in communion
Cult of Mithras
was born from a rock on Dec 25 and was immediately visited by shepherds
this cult had very similar practices to Christianity like baptism and communion
Cult of Isis
Very similar to the figure of the Virgin Mary
became sort of a ethical and giving god/goddess
~Scholars do not believe that without the mystery cults, the idea of Jesus would not have emerged- Jesus was a real person (can I get a good Amen
Early Life of Jesus
Born in Bethlehem
Bethlehem was very at odds with the Roman Empire
Bethlehem was a place where Christianity and Judaism met- place of cultural diversity
Teachings
Jesus spoke a message of peace- disagreed with the Zealots
Preached of a heavenly realm/ kingdom- not a political kingdom
lots of teachings follow Jewish texts but rather than preached of Yahweh he preached of himself and God the Father
Declared himself the Messiah
People were disappointed because he was’t a radical reformer
Sanhedrins saw Jesus as a threat because His preaching questioned authority
“Good works is fine but if your heart is in the wrong you are in the wrong”
As a result he would be put to death by the Roman Empire:
Pilate (ruler at the time) saw a potential volatile situation as the Jewish people were just liberated from the Egyptians and emotions were high» The Crucifixion
Paul of Tarsus (c 5-67)(The apostle Paul)
Formerly persecuted Christians but was reportedly converted to christianity
Was a Roman citizen and spoke many languages
became a converter/ preacher to Gentiles (Gentiles = non-christians)-
Opened it up to Gentiles- this was the key to the religion moving away from Judaism to Christianity
Jesus spoke in Parables whereas Paul’s teachings were a lot more grounded and less abstract
Paul’s argument: Judaism was a preparation for the Messiah/ Jesus
Paul: *persecutes Christians*
Also Paul:
Spreading of Christian Teachings
Spiritual equality under God - Found appealing by those enslaved and women which contributed to the spread of Christianity
The Rise of Papacy
Early Christianity
Romans honored and revered their gods because of how successful they were- their success indicates the legitimacy of their gods so other people worshipped their gods» Romans were VERY proud of their gods ⬇
Christians saw the roman gods as fake or possibly evil spirits ➡ romans were HIGHLY offended and outlawed Christianity because they saw the Christians as a threat because they believed the Christian’s would offend their gods and put their success at risk ⬇
All of this led to persecution:
Martyrs- people who die for religious purposes
Persecution was dramatized over the retellings throughout history
If you were Christian and kept your head down you could make it
They would later learn to live with each other
Christianity would start to become the more common religion by 375 CE as the roman empire power started to fade and by default the roman religion lost some of its cache
The Christian faith of this time believes that at any moment the second coming Jesus could be any second- you could turn around and he might be right there… ⬇
as a result it was very slow to develop but would eventually have higher- ups (bishops) that would claim the authority of correct doctrine (incorrect doctrine was seen as hearsay).
Specialness of Rome
Paul’s letter to the Romans would be very important in appointing Christian Doctrine
Christians in Rome had a lot of unity and political prestige- other christians would look up to them
“Doctrine of Petrine Succession” ➡ Doctrine of Peter- “you are the rock of which i will build my church” - Peter would become the First Bishop of Rome
his successors inheriting the authority and the responsibility being passed to them
By the 300-400 CE there was a decline in Imperial political authority- major power vacuums- this led to instability in the empire leading to the Pope stepping up and assuming some control» gains more political authority so people looked to him for stabilizing things
Fall of the Roman Empire
Many myths and mystique around the fall of the empire
it was a combination of internal issues that weakened the empire and led to the decline of power
Internal Problems
A LOT of border to protect
to the north there were the Germans and to the east there were Persians
problems within the military included there were not enough Italians to fill the army ranks- resorted to people outside of Italy but bc they were conquered people their loyalty was not guaranteed
people were loyal to the generals but the generals were not loyal to Roman Empire
often fighting between the generals over who would assume power next leading to dysfunctional constant sate of civil war and they are losing land consistently
Emperors were constantly losing their rule and being assassinated with no control over the military
Germans are knocking on the door causing havoc
Constant warfare= scared people= decline on agriculture= decline in surplus= economic decline ⬇
Trade, commerce, and agriculture grinds to a halt
mining operations decline so romans cut the silver content in the coin leading to inflation
Reforms
2 emperors were trying to stabilize things
Diocletian ( 284-305 CE)-
The empire is too big for one person to be in charge of it all
divided the empire up into two: the eastern roman empire (more greek) and the western roman empire
there were now two roman emperors along with a “Jr emperor” that watches and learns hands on how to run an empire
Constantine (306-337 CE)
wants power for himself and marched on Rome and meets his enemy at Milvian Bridge- there he saw a cross and words to march in the name of that symbol
as a result after victory we start to see a lot more pro-christian reforms- christian bishops would be exempt from taxes and there is not much christian persecution anymore
he would convert to christianity later on
persecution between pagans and Christians switches- now pagans are being persecuted and christians are accepted
Constantine would move the capital of the eastern roman empire and form Constantinople ( a new Rome) leaving Rome behind
Constantinople was be a pivotal and widely important city for christians
The eastern roman empire would continue on for hundreds of more years
western roman empire is now a shell of what it was with roman and would experience invasions
Barbarian Invasions
Germanic Peoples- seen as physically large and barbaric and intimidating, fighting was seen as part of their culture
romans would fight them but also try to assimilate them into their empire-
Empire in shamble so the pope steps in
Theodosius- a pope that would make Christianity the official religion, negotiate with the invaders, give land so they would not be killed- would not be super successful 0_0
Attila the Hun- would negotiate with the pope» emperor is frickin MIA apparently
By 476 AD a lot of land was given up to spare their lives and as a results a lot more kingdoms are showing up
Constant threat and present danger for the roman peoples sets up the beginning of Feudal Europe
Byzantine Empire
The Eastern Europe Empire would continue for another 1000 years before finally being conquered by the Ottoman Turks in the 1400s- Capital was Constantinople (now Istanbul)
Eastern Europe was “Roman” but culturally it was technically greek- thats why its called the Byzantine Empire
Sources of Byzantine Strength:
very strong military tradition
conquered lots of mediterranean and northern Africa
very good generals
The Capital of Constantinople had a great position (water on three sides)- hard for land armies to take it
they have the infrastructure necessary to protect their city from water attacks (complex system if walls that made it so the emperor would know who was entering the area)
Money was spent on Infrastructure ⬇
They had Cisterns- collects rain water- creates a reliable stable water supply
Preserved roman law but made it 🤩 better 🤩 - Justinian’s Code
Justinian’s Code:
Emperor Justinian (482-565) would bring in bright legal scholars to fix and clarify the Roman law
3 Parts to the Code:
the law
commentary on the law
guide book of civil procedure for law students
Byzantine was known for their literature and culture (still greek but little different) (they carry traditions of the Greco- Roman world)
Not much of innovators in the realm of science and medicine- they did create “Greek Fire” (a military weapon tactic)
Constantinople:
the largest and greatest Christian city that was pivotal for Christians
was a critical city for trade if you wanted anything from the east- very good trading partners with the east
Growth of the Christian Church
Emperor would divide their empire into dioceses (a territorial area part of a whole empire) and often put bishops in charge of these - this leads to the bishops gaining more and more power aside from the power of correct doctrine
Romans would want everyone on the same page with a decently universal doctrine to ensure political unity ➡ would lead to the Counsel of Nicene where they would write down the Nicene Creed (explains the Holy Trinity doctrine)» Solidifies the beliefs of the Christian religion and helps spread the belief of the Holy Trinity- 325 CE
Eastern and Western Churches:
The Pope in western Europe would step in a lot to communicate and negotiate and by the fall of Rome there is no one to challenge the Pope ➡ he would become the most important man of Europe
Pope of western Europe and emperor of eastern Europe don’t trust each other
the pope would get scholars together and create a general consensus for practices creating strong difference in practices in Rome and Greece- MAJOR tensions with lots of side eye and shade being thrown 😗
The emergence of different traditions would lead to several problems and conflicts and the emergence of the roman catholic traditions and greek orthodox church traditions
Charlemagne (768-814) Leader of Carolingian Dynasty
legendary for being a BIG man that loved horses and wealth (and women apparently )
illiterate (LOSER 😜)
legendary warrior and enslaved the people he conquered (mainly slavic people)
Spread christianity by whoever he conquered he converted
would become the King of France and would go to war with the Germans
“Spain is under control by Muslims, Pagans are ignored, Lomdbards are a threat, Britain is an outpost, but maybe Charlemagne cant bring everything together”- The Pope probably➡ so Pope Dictates him the Holy Roman Emperor
This would indicate BIG TIME that the Emperor of Rome is not the true emperor and this creates major differences between the Italy and Greece
Decline
Louis the Pious (son of Charlemagne) would succeed after the death of Charlemagne- very short rule
Louis’ sons would argue over being ruler and divide the kingdom into three
When the kingdoms would begin to lose power and tear themselves apart we would then see the vikings come into play
Rise of Islam
The Arabian Peninsula is verrryyy harsh conditions and very dry
People who lived in Arabia before Islam were called Bedouins- they had figured out how to cross the desert and were therefore excellent traders and merchants
Bedouins were tribal- there would be a lot of feuding among the bedouin tribes
Things will come down to tribal loyalty- NOT a place of political unity and peace
Mecca (place of the Ka’ba) would be the site for pagans, Jewish, and later Islamic people to worship and pay homage to polytheistic gods (for pagans) after crossing the desert- religiously diverse
Muhammad (570-632 CE)
was born in Mecca during a very unstable time
Volatile situation in Arabia gave rise to Islam-
Muhammad would experience poverty and being an orphan ➡ leads to certain beliefs (ex. giving to the poor)
Muhammad would be taken in by his uncle who would take him on his merchant travels and he would end up encountering a very diverse group of people
Muhammad did not like the fighting and was very disturbed by the conflicts
very spiritual person
one day when he went out to the woods to pray it is said he was visited by the angel Gabriel who delivered a direct revelation from God
that revelation would lead him to go out an preach the worship of one god (Allah)
the Quran was the pure holy book on the belief and submission to god
His Revelation: the word islam means submission to god; muslim means one who submits
he tried to go back to Mecca to preach his revelation and was repelled by the city leaders and {would eventually be expelled from mecca the period of time being known as Hijrah and is exiled to the city of Medina where there is a very straight forward polytheistic religion and he spreads the word of Islam} ⬇
Takeaway: he got everyone on the same page and united them under the muslim name without tribal differences in the way
Muhammad and his followers of Medina would go to war with Mecca and eventually take Mecca and destroy the idols while also giving thanks and forgiving his enemies- (I cant remember what he said but i think their success???) gave validity of the Islam faith to those outside of the faith making them more willing to adopt it.
Doctrines of Islam- 5 Tenets
Oneness of God
there is one all powerful god who one must submit to
Abraham built the Ka’ba in Mecca where angels used to worship and is the patriarch of the Arabic people and Islamic religion
Muhammad as a prophet
Muhammad believed that Jesus was a prophet and not divine- he thought that the teachings of Christianity had been mistranslated
People of the Book- how the islamic people describe Christians and Jews
Muhammad believed that he was the final prophet
Qur’an as the Word of God
the Qur’an is the final word of god- the final word is in Arabic and as a result is cannot be translated so as to protect it from being lost in translation
Belief in Angels
Site of worship for Angels was the Ka’ba
Life after death
Qur’an speaks of an afterlife and a day of judgement where the bad will. be punished and the good will be rewarded with there being a separation of good and evil
Five Pillars of Islam
Profession of Faith
there is no God but god and his prophet is Muhammad
Daily Prayer
muslims pray five times a day facing in the general direction of Mecca or if they are in Mecca they fave the Ka’ba
Charity- Almsgiving
if you are able to give to charity then you do so freely to help the poor/ less fortunate
Fasting during Ramadan
Ramadan is the holy month (starts the ninth crescent moon/ based on lunar calendar) of Islam and commemorates the month the Muhammad received his revelation from god
the very young, old, people with dietary restrictions, pregnant women, and menstruating women are not expected to fast during Ramadan
All holy scripture comes during this month
Pilgrimage to Mecca→ Hajj
you are to visit the city of Mecca and pray to the Ka’ba
if you are financially able, as part of the third pillar, you are to help finance or finance another person’s pilgrimage to mecca
this pilgrimage has caused Mecca today to be one of the most diverse country on earth
Islamic Expansion
the Islamic faith grows from being a religion to being an empire and will become the dominant religion at this time
The Islams would soon conquer the Byzantine Empire, the Persian Empire and the city of Alexandria
Jihad- “struggle”, in the muslim faith it is a personal struggle of a person in their sinful nature- theorized this contributed to the muslims being able to defeat the Persian and Byzantine Empire as a part of God’s will
Early Caliphates- political states/ empires
Caliphs- the administrator/ heads of the Caliphates
the Qur’an did not lay out clearly who would rule after Muhammad’s death
the Caliph would be Abu Bakr elected by Muhammad’s closest followers
there was fear that after Muhammad the religion would break apart and Bakr held it together in its infancy
Abu Bakr was a military, political, and religious leader that did a lot o for the empire
with him there is the establishment of the Caliph faith
The third Caliph was Uthman
authorized the copy of the Qur’an to be written down
comes from Mecca
was believed his family only converted for political convenience
Opposition of Uthman was Ali and argued that he should be Caliph
Uthman would be assassinated- wHo dId iT, wE’LL nEveR kNow :0
Sunnis v. Shi’ites
Ali
claimed he was personally familial bonded to Muhammad and was personally selected to be the Caliph
Mu’awiya would claim that Ali was not the true Caliph leading to a civil war in which Ali would be assassinated
Ali supporters would be called the Shi’ites- small minority that can be disruptive
Mu’awiya supporters would be called the Sunnis- majority
Sunni means “follow Muhammad’s example”
The split between the Shi’ites and the Sunnis caused extreme political division
Umayyad Dynasty
would get rid of the political election system because of how dangerous it was for the Sunnis
responsible for military expansion
expanded all the way to Spain and parts of China
At the time it was the largest empire the world had ever seen
Moved the capital from Medina to Damascus and everything under the Caliphs
conquered entire mediterranean under the Caliphs
top traders and old traders are revived
got everyone on the same page- gave people a financial incentive to convert (taxed non-muslims)
The Arabic would become very important for people (especially educated people) to know- Arabic becomes the next greek
Abbasid Dynasty
Abbasid family claimed that had familial connections to Muhammad and claimed they should be the caliph
encouraged factionalism and division until there will be a full scale revolt against the Umayyad
moved the capital from Damascus to Bagdad
Bagdad would be incredibly important and cosmopolitan city
political implications to moving the capital: they though the Umayyad was putting the Arabic culture above others by having the capital in Damascus
Abbasid was seen as good rulers which helped many people convert
Caliph is on top of society but is expected to make himself available to regular people
Ulama- islamic scholars who help the Caliph write the Sharia law which will include, religious issues, legal issues,
Qadis- are charged with enforcing the law
Diwan is the central political figure made to collect taxes and administer funds for charity
they recruited people from across the empire to work in the diwan because they didn’t care about someone being muslim, they just wanted good people working in their capital
created Provinces to have autonomy like the Persians- over time this would dilute the power of the Caliph- less of an emperor to more of a figure head
Vizier- the adviser to the caliph who would supervise the bureaucracy, the military, and economic processes
Islamic Society
Cosmopolitan
wide variety of diverse cultures
Arabic unites people in a common language
they are well versed in other cultures as they are exposed and educated
Islamic empire but many religions are practiced- there are no forced conversion here requiring tolerance on the part of the leaders
individual cultures just exist under Islamic empire
Social Mobility
there are still social classes but social mobility is more common
there was room to be born from nothing and become wealthy ← has to do with the Arabic heritage of being the “middle man” in trade on the silk road
Nobody:
Arabic Merchants:
merchants are high in society→ no negative connotation around “middle man” or “business man”
in Islamic religion everyone is the “same before god under Allah” which aids in social mobility as people can now envision themselves moving up in addition to making people more open to others below them moving up in society
Literacy
Around 20% of adult men can read- very high for this time
Wherever the empire expanded schools were built as men are expected to be able to read the Qur’an
Almsgiving also contributes to this as they are expected to give schools to the poor
Caliphs will require there to be Madrasas- a school for the study of Muslim law and religious science- so these future leaders can be well versed in Sharia ⬇
Sharia- the islamic legal code that includes interpretation of the Qur’an and applies islamic principled to daily life
there would even be scholarships
This leads to a very well educated society
They will import paper for education from china and make it better by adding starch to it which will spread to Europe
Tolerance
referring back to the People of the Book
what Muslims called Christians and Jews which means that they too only believe in one god
for the most part tolerant- any persecution of non-muslims is localized and sporadic (not common)
some Jewish people had wealthy and exalted position in society
Rigid moral code= patterns of more growth?
Inter-religious relationships are a thing 😗 and help create the cosmopolitan society
for scholars there is a positive context with this because sharing of ideas and education
Christians, Muslims, and Jews often trade with each other and share art
Status of Women
The society is still a Patriarchy
male dominated society
General improvement in the status of women in Arabia after Islam
Polygamy- multiple wives/ women← Muhammad was a believer of polygamy and had many wives which were held up and exemplified as examples of what a good muslim is
there are places for women in politics
Qur’an implies spiritual equality under Allah for men and women
ex: men are punished the same as women for cases like adultery
not unheard of for women to memorize and recite the Qur’an
However; women also became a form of status in the society with the more women men had the better their status
Veil for women- is not originally seen in the Qur’an- it is a mark of Persian status for upperclass women and a form of modesty
Burqa- the total body covering for women
Harem- translates to “forbidden”; refers to the women’s quarters of the home; symbol of male prestige for men to have a large harem of women to sleep with
Overall the status of women is very fluid
Culture
there will be preservation of classical greek culture by the Islamic empire
europeans largely failed at preserving the greek teachings of Aristotle, Plato, …. because they were pagans
Islamic people had no hang up in reading it and enjoyed a lot of Aristotle’s (and some of Plato’s) teachings
they looked at their teachings as the basis of knowledge and studied their teachings to try to understand how this society had such a strong basis of science→ even wrote commentaries on these original latin and greek texts :0
Science and Medicine→ they learned the concept of zero from India along with the concept of the decimal point» gave rise to Arabic numerals (12345….)
this is where algebra would start to take shape (crap ☹ )
Iba Sina- preeminent physician, compiled greco-roman knowledge on medicine and figured out Tuberculosis is contagious→ studied the spread of disease
was also a philosopher
Bagdad, Persia and other countries in Arabic Peninsula housed the best doctors in the world at this time
development of the hypodermic needles and cauterization
Philosophy
philosophers were expected to find a connection to logic and ones relationship with god
wrote about the ideal ruler based on logic
Sample Questions:
Which of the following did the greeks adapt from the Phoenicians?
the theory of the forms -the prisoners in the cave by Plato
phonetic alphabet
phalanx
Both b and c
Which of the following explains why the greek language and custom were important to the Hellenistic World?
They were common among educated people, which allowed ideas to spread
they provided governmental models
they facilitated trade across a wide geographic expanse
all of the above
Which of the following statements regarding Tiberius Gracchus is true?
He expanded the frontier of Rome into northern Britain
he unsuccessfully attempted to expand the frontier into northern Africa
he struggled to address the economic problems of the plebeians through land reform
all of the above
Which of the following did not contribute to the fall of the Roman Empire?
barbarian invasions
religious factionalism
economic crisis
weakened military
Which of the following does not help explain the strength and endurance of the byzantine empire?
they had no enemies
advantageous city position with water surrounding three sides of it
infrastructure with complex walls and aquifers
very strong army with strong army traditions
Which of the following is the correct definition for the word “Islam”?
“one who submits”
“followers of the prophet”
“submission to god”
“the word of god”
World History- Ancient Greece
Greeks were once Paleolithic and Neolithic too- started farming around 3200 BCE
Mycenaeans
1st well organized society in Greece (about 100 years after Hammurabi’s code)
spoke an Indo-European language
The Iliad, The Odyssey both were written about the Mycenaeans ^^
Minoans
Society located South of the Mycenaeans
very similar to the Mycenaeans (the Mycenaeans would pull a lot of their culture form the Minoans)
Centralized Kingdom » under one rule
Linked to Mycenaeans via trade, politics, culture, intermarriage
Based in trade » thrives in trading + economics
Writing developed for record keeping
Their records suggest government involvement in trade
Would eventually be conquered by the Mycenaeans
«Mycenaean Society would collapse around 1200 BCE»
Greek Dark Ages: goes from large kingdom to more tribal set up » would be decentralized for the next 500 Years
Greek City States- (similar but different from the ones of Mesopotamia)
The original tribes will grow to be independent City States called The Polis
Nature of the Polis:
there was a focus on community- everyone has an important role
Self Identity is very tied to your Polis- you are your Polis
Acropolis- the center of the Polis with many religious buildings
There is no political unity but saw themselves as under that culture with outsiders being Barbarians
Different Poleis had different systems of Government including:
Monarchy
Oligarchy
Aristocracy
Democracy (Athens)
Even with these few generalized government systems every Polis government is different
Greeks thought of Democracy as an ineffective way of government » thought it was only suited for smaller city-states
Geographic Influence on Greece:
farming took much longer for the Greeks to discover and develop because of Greece’s rocky mountain terrain
created poor farming
this leads to the creation of a maritime culture leading to trade being essential » they become excellent merchants
poor communication
difficult rivers to navigate
City States become Isolated
Limited Farming
this created very bound/ close families depending on each other for survival
Geography causes a lack of Political Unity but excellent sailors and merchants
Greek Colonization - they spread out largely over the Mediterranean (wherever they could sail to)
did so for the sake of trade»
did so for exilement
»Trade»
They did not have great agriculture but what they did grow was highly in demand:
Olives> oil
Grapes> wine
Because of trade- social status is not based on landownership leading to a small but powerful middle class that will start growing larger
The Greeks would learn from other Cultures also…
The Phoenicians
Known for their alphabet based on phonics
The Greeks would adopt this alphabet of phonics which would be revolutionary for the culture- much easier to learn»
»Social Effects of the Alphabet»
There were no “Scribes” because now anyone can learn to read now- not everyone did know but now it was much easier to
Literacy and numbers becomes essential for trade across the sea
The Middle Class would start to perpetuate their status through education- allows their children to keep that class or move up
This leads to an educated society
Middle class will play a huge role in democracy- middle class will demand a political seat and be denied by the wealthy » conflict leads to democracy» Athens
»Athens»
Athens did not start out as a democracy- originally an aristocracy
Athens is unique because it had a smaller (but growing) middle class that would feel the pressure of the cities trying to get land.
Upper class will push middle class down trying to gain as much wealth through trade
Middle Class land owners having to sell themselves to slavery to pay off debts
Central Figure: Draco
An elite that felt the worry of the angered middle class» leads to the Draconian Legal Code
Excessively difficult and cruel punishments
Favored the elites but everyone was under the law
does not solve the crisis of those sliding into slavery
somewhat diminishes the class differences
now because of the code and debt people were frequently sent away (exiled)
Central Figure: Solon (comparatively opposite to Draco)
Solon was an elite that felt sympathy for the middle class- reformer
He publicly recited poems that prompted some sympathy for the poor by the elites
Solon would go on to:
free those enslaved
abolish slavery stemming from debt
brings back those that are exiled
allows commoners into government
“everyone” could now vote on laws and discuss them» revolutionary because now change could come through democracy without a revolution, conspiracy or violence
Athens will face pressure from limited resources and this will lead to colonization
Greek Wartime Innovations
Sense of community in the Polis leads to fighting FOR the Polis and defending the Polis ~Polis is love, Polis is life 😍~
Greek would get very good at Calvary (soldiers fighting on horseback)
Greeks will become innovators in warfare due to competition over resources:
Greek Phalanx- based on training and discipline» intimidating to enemies ~jumpscarrrree~
Diminishes the individual to emphasize the greater whole of the Polis
Greek Hoplite- heavily armored soldier that was very well trained, equipped with a spear, and many weapons and backed by infantry
this would be very effective
Spartan Militarism
Militaristic Society- best, most brilliant warriors of Greece
Similar pressures as the athenians- limited food, and fast growing population- conquers and enslaves the Helots to gain resources and force them in slavery
Helots are constantly rebellious and hate the spartans-
Spartans are consistently worried that any day there will be an uprising and the helots will kill them
spartans had to become very good warriors because constant fighting and worrying over the helots
Started out as a monarchy with a aristocracy
Sparta middle class (men) will eventually gain political rights after threatening to let the helots riot and rebel- commoners are the spartan military- (feel the upper class owes them something for keeping the wealthy from experiencing the wrath of the Helots )
Started out as a monarchy and developed to 2 kings were part military leaders that would be elected by the people- had advisors/ counselors around them
Spartans were expected to set aside desires, individual wants and needs aside for the good of the city
“better to be dead than to surrender”
revered by other greeks for being the best warrior society
Men were gone training for fighting a lot of the time- almost absolutely no men
this leads to women managing the estates and giving order to the helots
women could own their own property
women could move about freely with very little control over their lives (sorta??)
Greeks in Asia Minor
Persian Wars
Persians want to control the trade of Greece up to the black sea to Ukraine- VERY desirable resources (breadbaskets)
Persian army had conquered almost all of asian minor- including some greeks
despite Persians being very convincing, the conquered greeks were very unhappy under their rule and described the Persians as barbaric
When the Greeks finally revolt against the Persians the Athenians want to help
Ruler Darius wants to crush the revolt and rule over Greece
very confident in his army, couldn’t even imaging losing to Greece- lost anyway (LOSER 😛 )
His son Darius would invade Athens
Athenians would be able to decide the fight of the battle- major advantage that lets them set traps»
Forced Persians to cross swamp land- renders horses useless and athenians won^^
leaves Persians bitter and wanting revenge
Darius’s son Xerxes would then continue the fight ^
Greeks aren’t naive so Athenians inform the other city states that they need to unify to form a strong alliance against the Persians»
Formation of the Delian League- Main Goals:
protect Greece from the Persians
Liberate the greeks from Persian control
Pericles of Athens will be the main leader- uses the league to build up the Athenian Wealth
this creates resentment from the other city states though because now athenians are so much more powerful and wealthy and other city states are worried athenians will subjugate them under their rule
Spartans are also angry at Athenians and refuse to ever submit under their rule
Persians will eventually lose war
Athenians want to keep the league but the other city states become angry because they don’t want to be under Athenian rule
as a result, Athens and Sparta will go to war- both find allies and rip Greece apart by side picking» Peloponnesian War
Spartans encourage revolt and eventually claim victory but the region is exhausted and trade has ground to a halt
This tragedy will lead to reflection and the creation of great art
Greek Philosophy
Art, dramas, philosophy, literature
Socrates (470-399 BCE)
Urged self reflection- “Know thyself”
“the unexamined life is not worth living”
no virtue in doing things because of tradition and being told to do things
Knowledge is virtue- knowing thyself is the basis of all knowledge
was previously exiled from Greece for a long while
teaches through a series of dialogues and ethical questions with no predetermined answers- Socratirial Method
may not know facts but an educated person will know themselves
Plato (427-347 BCE)- student of Socrates that wrote everything down for him
An idealist
wants to understand the nature of reality and what reality is
“what is real?” Concerned with the nature of truth
Believe there is two worlds: 1) one where we observe the world through our own lens- Our reality- human flaws and human frails 2) other world that is perfect and reflects a true unchanging reality- the perfect ideal of the world with nothing is wrong; the ultimate reality
This world is a distortion of a perfect world
the flaws of the world reflects our flaws and out there is a realm with the ideal world
Example of this ideology: a chair in our world is “not a real chair but rather an imperfect derivative of the ideal chair with no flaws”
Lays out an ideal republic- why model a government based off flawed government?- don’t study imperfect models, study the perfect ideal
Platos allegory of the cave: we are all the prisoners held captive by our own reality and only seeing imperfect reflections of what is real
Only by becoming enlightened (by mediating on the ideal) can we see the world for what it really is and see true reality
Aristotle (384-322 BCE)- student of plato
More interested in the observable, measurable reality
believes knowledge comes from analyzing the real world
collecting and learning more facts leads to real knowledge (much of the scientific method comes from him)
don’t just study abstract method- the answer lies in the nature of the real world
Poet, philosopher, scientists chemist
analyzes and separates the different forms of government that different greek city states
believes the planet is composed of 5 elements (fire, earth, water, air, and ether (stuff the universe is made up of)
Earth is at the center of the universe and everything orbits it
Closely examining the photo gives good representation of the beliefs of Aristotle (right) and Plato (left)

Hellenistic Society
Bigger and like the greeks but not greek
Alexander the Great- conquers the known world by the age of 32
mystique, charm, romanticized
greek became the common language of the land he conquered- conquered all the way to some parts of India
influence will be mainly cultural
personal tutor was Aristotle but he’s still not Greek
Rise of Macedon
Macedon is cultural cousins to greek
Philip II of Macedon was ruler of Macedon and father of Alexander the great
Unhappy with the Peloponnesian war between the Athenians and the Spartans because of effects on trade
Plans to conquer and invade Greece since the Persians could not
uses the lack of the Delian league and lack of unity to politically conquer Greece- strategically severs any alliances and takes advantage of distrust
Got the greeks to buy into his rule by going to war with Persians to liberate the Greeks under the Persian rule- is promptly assassinated
Alexander the Great would be responsible for eliminating any threat (other people) to his chance of taking the thrown
Once king he will be responsible for liberating the Ionians (greeks under Persian rule)
Worshipped Egyptian gods to show respect- he’s polytheistic so what’s a few more gods 🤷♀
Crossed the Indus river valley and conquered the rest of the known world
partying and drinking would eventually kill him
there could be no empire without him and there would be a 40 year civil war among his generals over who would rule
Alexander’s kingdom would them be divided into 3 political units- still a Hellenistic kingdom
no political unity but culturally unity and trade
Leadership and elites speak greek- basically if they were important they would speak greek »
Trade will be based on greek culture
Hellenistic society was extremely cosmopolitan (knowledgeable of the world around them)
Hellenistic society was very multicultural (culturally hellenistic but must embrace diversity to maintain power)
» With a majority of people speaking greek, trade and spreading of science and culture would be unified and happen much more easily»
“Hellen” = greek “istic”= like } Greek like but still Macedonian- blending of cultures
Alexander the great known for establishing cities~ One way different cultures would be Hellenized
Once Alexander died, the government officials would continue the tradition of colonization spreading greek culture VERY far (some statues of Buddha look like Alexander)
Spread of roads, bridges, and harbors for trade- greek infrastructure spreading
»Emphasis on NO political unity but very much CULTURAL and ECONOMIC unity (cant emphasize this enough apparently)
» With a majority of people speaking greek, trade and spreading of science and culture would be unified and happen much more easily»
City of Alexandria
Library of Alexandria- burns to the effing ground apparently
Common language would lead to the spread of science and further development of different philosophies
Epicureanism- for that time period, it is a philosophy that says the meaning of life lies in seeking pleasures (not just of the flesh but also the avoidance of pain)- do so by ignoring politics, looking into your own feelings (escapism philosophy), letting go of what causes them pain or discomfort
Stoicism- believed that personal achievements don’t matter and the meaning to live is to live a very virtuous life;
accept and endure the bad parts of life; first to articulate the brotherhood of life-”we are all in this together”;
first to articulate the idea of Natural Law: There are natural laws in the universe that dictate how life happens on earth- if you understand the natural laws you can better understand the world and how to live in it
All humans are kin; we need to learn to live in harmony with one another and endure the rough patches in life
Key Figure: Zeno (335-262 BCE)
Hellenistic Scientists
Aristarchus (310-230 BCE): Astronomer; figured out the reasoning of why mercury looked like it was going backwards: the sun was the center of the solar system and everything orbited around it
Euclid (300BCE): Mathematician- studied Geometry; worked in the library of Alexandria; we
Archimedes (287-212 BCE): soldier and inventor and mathematician; invented the compound pully to lift weights; the archimedes screw; articulated the principle of water displacement is equal to the weight of the solid object displacing it
Roman Empire
Nobody:
Romans:

Etruscans
Hail form northern Italy
Would encounter and trade with the greeks- strong dose of greek culture now
They are nomadic and will eventually settle on the edge of the Tiber River
previously occupied by the Latins which will be conquered by the Etruscans
elites will be Etruscans and commoners will be Latins
Will have a lot of trade with greeks- will adopt the greek alphabet and adapt it to the Latin alphabet of the 26 letters
»Not a lot of solid information about this time period- a lot of “information” is based in mythology- we do know there was a king that would be other thrown and the Roman Republic would start»
Roman Republic
had a larger population and spread out more- therefore would not have democratic features
Assemblies to elect leader but the power was very tipped towards the elites and wealthy
Patricians- wealthy land owners and military leaders- would make up the Senate
the senate was an aristocratic system that had the power of the purse
The Consuls- an executive office; had executive power; was elected by the senate, senate attempted to act as advisors to the consuls
Rome would be a society based on the law and nobody was above the law- all people and all societies should be under the same law
Rome made firm distinctions between civil disputes and criminal disputes
Roman law would try to find a fair solution for all parties involved in disputes
Roman law will be rooted in logic rather than tradition
Struggle of the Order
Plebeians- anybody that wasn’t enslaved but wasn’t wealthy or elite- does not like the Patricians
wants a far equal voice in government
leads to tension and fight from the Plebeians- would later go on strike to make a point
Big problem for the Patricians because plebeians are the backbone of society
Patricians would allow them to express grievances grievances in court
Plebeians would battle for a more fair written law leading to everyone knowing their rights and the law
Can argue cases before the court
Equal before the law around 280BCE
Written Law» the Twelve Tables
Roman Expansion
would adopt and adapt the greek gods as their Roman gods (ie Jupiter, Mars…)
would build stone bridges and roads to incorporate Italian peninsula
Dispute with plebeians» Citizenship matters- romans would grant citizenship to those outside of Rome
Citizenship would soon become a symbol of status» some would even voluntarily enslave themselves to work for a few years to later be set free and become a citizen
However: Rome would not make citizenship universal- they viewed it as a privilege not a right (would take it away if they feel it deserved)
Will expand for the sake of needing more resources to feed growing cities
Origins of Imperialism
any external threat to the Roman power would be seen as an existential threat- “we need to destroy them before they destroy us”
that threat would become the Carthaginians - great tension and competition
Carthaginians would be ethnically Phoenician
More than romans, Carthage would feel the demographic pressure due to being strictly maritime and in need of resources from the North (where the Romans were) (South was not an option as that was where the Egyptian desert was)
these tensions and need fore resources leads to the Punic wars
Punic Wars (264-133 BCE)-Series of long drawn out wars between Carthage and Rome
Romans would build up their navy and take Sicily from the Carthaginians
Would set up Provinces in captured territories leading to a weakening of the institution (first province was Sicily)
Hannibal- leader of Carthage during the wars that led the march into southern Italy (on elephants :0 )
Rome would march in behind them to retake Spain and cut off their supplies; would then move on Carthage and cause Hannibal to leave Italy to defend the city
Results and Effects of the Punic Wars
Rome would win and be able to feed itself- first step to becoming an empire :0
Spoils of war were plentiful- got amazing wealth, gold, and enslaved people
Aqueducts would be a new invention along with new public facilities (bath houses, gymnasiums, libraries, etc)
Territory would be divided up into Latifundas
Massive Plantations run by Patricians and worked by enslaved people
these Latifundas put Plebeian farmers into a tight spot since they would be undercut by Patrician farms and since they would have to repair their land after being gone in war for years- would end up having to sell their land to the Patricians and moving to Rome
creates a growing poor population in Rome and lots of disorder
Leads to the creation of more public works like circuses to try and keep a lid on the chaos as veterans flood into the city (cuz that will fix it 😃 👍)
Tiberius Gracchus
elected consul member who would call for land reform to limit the size of these Latifunda and redistribute the rest of this land to the poor to get them out of the city
would be murdered by angry Patricians (RIP 💀 )
His brother Gaius Gracchus who would also try to bring reform would be murdered too
There is severe tension because these war veterans are getting no more than bread
The Romans government is not adapting - leads to a civil war
Roman Civil War
Because communication was so hard in this civil war the “guard rails” would be taken off generals so they could do what they needed to do (or what they wanted to do (AKA conquer Rome)) (seriously who thought that was a good idea??)
Sulla (138-78 BCE)
Set himself up as a dictator in Rome for about 9 years
tried to reform the system and reestablish the republic but would not really be successful
Pattern of conquering hero takes Rome, rules, and it repeats
looking more and more like an empire with imperialism
Pompey (106- 48 BCE)
would conquer all of modern Spain
allied himself with Julius Caesar- would eventually have a falling out and kick Caesar out
Julius Caesar (100-44 BCE)
Conquered modern day France (Ghall)
Would start to campaign and later assassinate Pompey
Bring back Cleopatra (69-30 BCE) after his campaign looking for Pompey
tried to use his power to help the Plebeians and restore stability (rules for 1 year)
colonized areas in Africa
abused his power
Brutus (85-42)
was pardoned by Caesar and thought of by Caesar as a little brother
was close with Caesar however thought he was Dangerous leading to him joining the conspirators and aiding in the Assassination of Julies Caesar (44 BCE)
now there is a power grab as all stability is thrown out the effing window
Mark Anthony and Augustus (Octavian) would fight for the control of Rome
Octavian is based out in the west (campaigns for Italian Nationalism)
Mark Anthony will marry Cleopatra and control Egypt and Greece (campaigns himself as a liberator of Greece and Egypt)
Mark Anthony and Cleopatra will have a Romeo and Juliet moment leading to the victory of Octavius and the death of the Republic
Imperialism society will emerge
Pax Romana- “The Roman Peace”
“The glory days of Rome”- the Hellenized empire
Greco-Roman empire

Rise of Christianity
Jesus of Nazareth (4 BCE- 33 CE) Context
Jesus was born in the land of Judea which had a lot of conflict with Rome- current king was Tiberius
Judea and Rome
Very violent times- Judea and Rome would not get along- religious tensions because the hebrews would reject Roman gods
Romans did not comprehend the idea of monotheism; lot of cultural misunderstandings
additionally there was a revolt in Judea of Roman culture
Hebrews found the Romans were greedy and violent
Romans saw Judea as a constant problem so they positioned a permanent army there and made the people of Judea pay higher taxes as a result
Sanhedrin
Jewish Elites put in charge by the Romans to handle the public and collect taxes
Zealots
political groups that wanted to force the romans out of Judea and would conduct political assassinations of roman officers
Messiah
John the Baptist would prophetically announce the Messiah was close at hand- people were expecting a political, military general not a preacher
Hellenistic Mystery Cults
secret religious groups in the Greco-Roman world
it is believed that these groups had an influence in the writing of scripture
Cult of Dionysus
lots of parallelism of the Father and Son telling of Christianity in the story of Dionysus
also partook in communion
Cult of Mithras
was born from a rock on Dec 25 and was immediately visited by shepherds
this cult had very similar practices to Christianity like baptism and communion
Cult of Isis
Very similar to the figure of the Virgin Mary
became sort of a ethical and giving god/goddess
~Scholars do not believe that without the mystery cults, the idea of Jesus would not have emerged- Jesus was a real person (can I get a good Amen
Early Life of Jesus
Born in Bethlehem
Bethlehem was very at odds with the Roman Empire
Bethlehem was a place where Christianity and Judaism met- place of cultural diversity
Teachings
Jesus spoke a message of peace- disagreed with the Zealots
Preached of a heavenly realm/ kingdom- not a political kingdom
lots of teachings follow Jewish texts but rather than preached of Yahweh he preached of himself and God the Father
Declared himself the Messiah
People were disappointed because he was’t a radical reformer
Sanhedrins saw Jesus as a threat because His preaching questioned authority
“Good works is fine but if your heart is in the wrong you are in the wrong”
As a result he would be put to death by the Roman Empire:
Pilate (ruler at the time) saw a potential volatile situation as the Jewish people were just liberated from the Egyptians and emotions were high» The Crucifixion
Paul of Tarsus (c 5-67)(The apostle Paul)
Formerly persecuted Christians but was reportedly converted to christianity
Was a Roman citizen and spoke many languages
became a converter/ preacher to Gentiles (Gentiles = non-christians)-
Opened it up to Gentiles- this was the key to the religion moving away from Judaism to Christianity
Jesus spoke in Parables whereas Paul’s teachings were a lot more grounded and less abstract
Paul’s argument: Judaism was a preparation for the Messiah/ Jesus
Paul: *persecutes Christians*
Also Paul:
Spreading of Christian Teachings
Spiritual equality under God - Found appealing by those enslaved and women which contributed to the spread of Christianity
The Rise of Papacy
Early Christianity
Romans honored and revered their gods because of how successful they were- their success indicates the legitimacy of their gods so other people worshipped their gods» Romans were VERY proud of their gods ⬇
Christians saw the roman gods as fake or possibly evil spirits ➡ romans were HIGHLY offended and outlawed Christianity because they saw the Christians as a threat because they believed the Christian’s would offend their gods and put their success at risk ⬇
All of this led to persecution:
Martyrs- people who die for religious purposes
Persecution was dramatized over the retellings throughout history
If you were Christian and kept your head down you could make it
They would later learn to live with each other
Christianity would start to become the more common religion by 375 CE as the roman empire power started to fade and by default the roman religion lost some of its cache
The Christian faith of this time believes that at any moment the second coming Jesus could be any second- you could turn around and he might be right there… ⬇
as a result it was very slow to develop but would eventually have higher- ups (bishops) that would claim the authority of correct doctrine (incorrect doctrine was seen as hearsay).
Specialness of Rome
Paul’s letter to the Romans would be very important in appointing Christian Doctrine
Christians in Rome had a lot of unity and political prestige- other christians would look up to them
“Doctrine of Petrine Succession” ➡ Doctrine of Peter- “you are the rock of which i will build my church” - Peter would become the First Bishop of Rome
his successors inheriting the authority and the responsibility being passed to them
By the 300-400 CE there was a decline in Imperial political authority- major power vacuums- this led to instability in the empire leading to the Pope stepping up and assuming some control» gains more political authority so people looked to him for stabilizing things
Fall of the Roman Empire
Many myths and mystique around the fall of the empire
it was a combination of internal issues that weakened the empire and led to the decline of power
Internal Problems
A LOT of border to protect
to the north there were the Germans and to the east there were Persians
problems within the military included there were not enough Italians to fill the army ranks- resorted to people outside of Italy but bc they were conquered people their loyalty was not guaranteed
people were loyal to the generals but the generals were not loyal to Roman Empire
often fighting between the generals over who would assume power next leading to dysfunctional constant sate of civil war and they are losing land consistently
Emperors were constantly losing their rule and being assassinated with no control over the military
Germans are knocking on the door causing havoc
Constant warfare= scared people= decline on agriculture= decline in surplus= economic decline ⬇
Trade, commerce, and agriculture grinds to a halt
mining operations decline so romans cut the silver content in the coin leading to inflation
Reforms
2 emperors were trying to stabilize things
Diocletian ( 284-305 CE)-
The empire is too big for one person to be in charge of it all
divided the empire up into two: the eastern roman empire (more greek) and the western roman empire
there were now two roman emperors along with a “Jr emperor” that watches and learns hands on how to run an empire
Constantine (306-337 CE)
wants power for himself and marched on Rome and meets his enemy at Milvian Bridge- there he saw a cross and words to march in the name of that symbol
as a result after victory we start to see a lot more pro-christian reforms- christian bishops would be exempt from taxes and there is not much christian persecution anymore
he would convert to christianity later on
persecution between pagans and Christians switches- now pagans are being persecuted and christians are accepted
Constantine would move the capital of the eastern roman empire and form Constantinople ( a new Rome) leaving Rome behind
Constantinople was be a pivotal and widely important city for christians
The eastern roman empire would continue on for hundreds of more years
western roman empire is now a shell of what it was with roman and would experience invasions
Barbarian Invasions
Germanic Peoples- seen as physically large and barbaric and intimidating, fighting was seen as part of their culture
romans would fight them but also try to assimilate them into their empire-
Empire in shamble so the pope steps in
Theodosius- a pope that would make Christianity the official religion, negotiate with the invaders, give land so they would not be killed- would not be super successful 0_0
Attila the Hun- would negotiate with the pope» emperor is frickin MIA apparently
By 476 AD a lot of land was given up to spare their lives and as a results a lot more kingdoms are showing up
Constant threat and present danger for the roman peoples sets up the beginning of Feudal Europe
Byzantine Empire
The Eastern Europe Empire would continue for another 1000 years before finally being conquered by the Ottoman Turks in the 1400s- Capital was Constantinople (now Istanbul)
Eastern Europe was “Roman” but culturally it was technically greek- thats why its called the Byzantine Empire
Sources of Byzantine Strength:
very strong military tradition
conquered lots of mediterranean and northern Africa
very good generals
The Capital of Constantinople had a great position (water on three sides)- hard for land armies to take it
they have the infrastructure necessary to protect their city from water attacks (complex system if walls that made it so the emperor would know who was entering the area)
Money was spent on Infrastructure ⬇
They had Cisterns- collects rain water- creates a reliable stable water supply
Preserved roman law but made it 🤩 better 🤩 - Justinian’s Code
Justinian’s Code:
Emperor Justinian (482-565) would bring in bright legal scholars to fix and clarify the Roman law
3 Parts to the Code:
the law
commentary on the law
guide book of civil procedure for law students
Byzantine was known for their literature and culture (still greek but little different) (they carry traditions of the Greco- Roman world)
Not much of innovators in the realm of science and medicine- they did create “Greek Fire” (a military weapon tactic)
Constantinople:
the largest and greatest Christian city that was pivotal for Christians
was a critical city for trade if you wanted anything from the east- very good trading partners with the east
Growth of the Christian Church
Emperor would divide their empire into dioceses (a territorial area part of a whole empire) and often put bishops in charge of these - this leads to the bishops gaining more and more power aside from the power of correct doctrine
Romans would want everyone on the same page with a decently universal doctrine to ensure political unity ➡ would lead to the Counsel of Nicene where they would write down the Nicene Creed (explains the Holy Trinity doctrine)» Solidifies the beliefs of the Christian religion and helps spread the belief of the Holy Trinity- 325 CE
Eastern and Western Churches:
The Pope in western Europe would step in a lot to communicate and negotiate and by the fall of Rome there is no one to challenge the Pope ➡ he would become the most important man of Europe
Pope of western Europe and emperor of eastern Europe don’t trust each other
the pope would get scholars together and create a general consensus for practices creating strong difference in practices in Rome and Greece- MAJOR tensions with lots of side eye and shade being thrown 😗
The emergence of different traditions would lead to several problems and conflicts and the emergence of the roman catholic traditions and greek orthodox church traditions
Charlemagne (768-814) Leader of Carolingian Dynasty
legendary for being a BIG man that loved horses and wealth (and women apparently )
illiterate (LOSER 😜)
legendary warrior and enslaved the people he conquered (mainly slavic people)
Spread christianity by whoever he conquered he converted
would become the King of France and would go to war with the Germans
“Spain is under control by Muslims, Pagans are ignored, Lomdbards are a threat, Britain is an outpost, but maybe Charlemagne cant bring everything together”- The Pope probably➡ so Pope Dictates him the Holy Roman Emperor
This would indicate BIG TIME that the Emperor of Rome is not the true emperor and this creates major differences between the Italy and Greece
Decline
Louis the Pious (son of Charlemagne) would succeed after the death of Charlemagne- very short rule
Louis’ sons would argue over being ruler and divide the kingdom into three
When the kingdoms would begin to lose power and tear themselves apart we would then see the vikings come into play
Rise of Islam
The Arabian Peninsula is verrryyy harsh conditions and very dry
People who lived in Arabia before Islam were called Bedouins- they had figured out how to cross the desert and were therefore excellent traders and merchants
Bedouins were tribal- there would be a lot of feuding among the bedouin tribes
Things will come down to tribal loyalty- NOT a place of political unity and peace
Mecca (place of the Ka’ba) would be the site for pagans, Jewish, and later Islamic people to worship and pay homage to polytheistic gods (for pagans) after crossing the desert- religiously diverse
Muhammad (570-632 CE)
was born in Mecca during a very unstable time
Volatile situation in Arabia gave rise to Islam-
Muhammad would experience poverty and being an orphan ➡ leads to certain beliefs (ex. giving to the poor)
Muhammad would be taken in by his uncle who would take him on his merchant travels and he would end up encountering a very diverse group of people
Muhammad did not like the fighting and was very disturbed by the conflicts
very spiritual person
one day when he went out to the woods to pray it is said he was visited by the angel Gabriel who delivered a direct revelation from God
that revelation would lead him to go out an preach the worship of one god (Allah)
the Quran was the pure holy book on the belief and submission to god
His Revelation: the word islam means submission to god; muslim means one who submits
he tried to go back to Mecca to preach his revelation and was repelled by the city leaders and {would eventually be expelled from mecca the period of time being known as Hijrah and is exiled to the city of Medina where there is a very straight forward polytheistic religion and he spreads the word of Islam} ⬇
Takeaway: he got everyone on the same page and united them under the muslim name without tribal differences in the way
Muhammad and his followers of Medina would go to war with Mecca and eventually take Mecca and destroy the idols while also giving thanks and forgiving his enemies- (I cant remember what he said but i think their success???) gave validity of the Islam faith to those outside of the faith making them more willing to adopt it.
Doctrines of Islam- 5 Tenets
Oneness of God
there is one all powerful god who one must submit to
Abraham built the Ka’ba in Mecca where angels used to worship and is the patriarch of the Arabic people and Islamic religion
Muhammad as a prophet
Muhammad believed that Jesus was a prophet and not divine- he thought that the teachings of Christianity had been mistranslated
People of the Book- how the islamic people describe Christians and Jews
Muhammad believed that he was the final prophet
Qur’an as the Word of God
the Qur’an is the final word of god- the final word is in Arabic and as a result is cannot be translated so as to protect it from being lost in translation
Belief in Angels
Site of worship for Angels was the Ka’ba
Life after death
Qur’an speaks of an afterlife and a day of judgement where the bad will. be punished and the good will be rewarded with there being a separation of good and evil
Five Pillars of Islam
Profession of Faith
there is no God but god and his prophet is Muhammad
Daily Prayer
muslims pray five times a day facing in the general direction of Mecca or if they are in Mecca they fave the Ka’ba
Charity- Almsgiving
if you are able to give to charity then you do so freely to help the poor/ less fortunate
Fasting during Ramadan
Ramadan is the holy month (starts the ninth crescent moon/ based on lunar calendar) of Islam and commemorates the month the Muhammad received his revelation from god
the very young, old, people with dietary restrictions, pregnant women, and menstruating women are not expected to fast during Ramadan
All holy scripture comes during this month
Pilgrimage to Mecca→ Hajj
you are to visit the city of Mecca and pray to the Ka’ba
if you are financially able, as part of the third pillar, you are to help finance or finance another person’s pilgrimage to mecca
this pilgrimage has caused Mecca today to be one of the most diverse country on earth
Islamic Expansion
the Islamic faith grows from being a religion to being an empire and will become the dominant religion at this time
The Islams would soon conquer the Byzantine Empire, the Persian Empire and the city of Alexandria
Jihad- “struggle”, in the muslim faith it is a personal struggle of a person in their sinful nature- theorized this contributed to the muslims being able to defeat the Persian and Byzantine Empire as a part of God’s will
Early Caliphates- political states/ empires
Caliphs- the administrator/ heads of the Caliphates
the Qur’an did not lay out clearly who would rule after Muhammad’s death
the Caliph would be Abu Bakr elected by Muhammad’s closest followers
there was fear that after Muhammad the religion would break apart and Bakr held it together in its infancy
Abu Bakr was a military, political, and religious leader that did a lot o for the empire
with him there is the establishment of the Caliph faith
The third Caliph was Uthman
authorized the copy of the Qur’an to be written down
comes from Mecca
was believed his family only converted for political convenience
Opposition of Uthman was Ali and argued that he should be Caliph
Uthman would be assassinated- wHo dId iT, wE’LL nEveR kNow :0
Sunnis v. Shi’ites
Ali
claimed he was personally familial bonded to Muhammad and was personally selected to be the Caliph
Mu’awiya would claim that Ali was not the true Caliph leading to a civil war in which Ali would be assassinated
Ali supporters would be called the Shi’ites- small minority that can be disruptive
Mu’awiya supporters would be called the Sunnis- majority
Sunni means “follow Muhammad’s example”
The split between the Shi’ites and the Sunnis caused extreme political division
Umayyad Dynasty
would get rid of the political election system because of how dangerous it was for the Sunnis
responsible for military expansion
expanded all the way to Spain and parts of China
At the time it was the largest empire the world had ever seen
Moved the capital from Medina to Damascus and everything under the Caliphs
conquered entire mediterranean under the Caliphs
top traders and old traders are revived
got everyone on the same page- gave people a financial incentive to convert (taxed non-muslims)
The Arabic would become very important for people (especially educated people) to know- Arabic becomes the next greek
Abbasid Dynasty
Abbasid family claimed that had familial connections to Muhammad and claimed they should be the caliph
encouraged factionalism and division until there will be a full scale revolt against the Umayyad
moved the capital from Damascus to Bagdad
Bagdad would be incredibly important and cosmopolitan city
political implications to moving the capital: they though the Umayyad was putting the Arabic culture above others by having the capital in Damascus
Abbasid was seen as good rulers which helped many people convert
Caliph is on top of society but is expected to make himself available to regular people
Ulama- islamic scholars who help the Caliph write the Sharia law which will include, religious issues, legal issues,
Qadis- are charged with enforcing the law
Diwan is the central political figure made to collect taxes and administer funds for charity
they recruited people from across the empire to work in the diwan because they didn’t care about someone being muslim, they just wanted good people working in their capital
created Provinces to have autonomy like the Persians- over time this would dilute the power of the Caliph- less of an emperor to more of a figure head
Vizier- the adviser to the caliph who would supervise the bureaucracy, the military, and economic processes
Islamic Society
Cosmopolitan
wide variety of diverse cultures
Arabic unites people in a common language
they are well versed in other cultures as they are exposed and educated
Islamic empire but many religions are practiced- there are no forced conversion here requiring tolerance on the part of the leaders
individual cultures just exist under Islamic empire
Social Mobility
there are still social classes but social mobility is more common
there was room to be born from nothing and become wealthy ← has to do with the Arabic heritage of being the “middle man” in trade on the silk road
Nobody:
Arabic Merchants:
merchants are high in society→ no negative connotation around “middle man” or “business man”
in Islamic religion everyone is the “same before god under Allah” which aids in social mobility as people can now envision themselves moving up in addition to making people more open to others below them moving up in society
Literacy
Around 20% of adult men can read- very high for this time
Wherever the empire expanded schools were built as men are expected to be able to read the Qur’an
Almsgiving also contributes to this as they are expected to give schools to the poor
Caliphs will require there to be Madrasas- a school for the study of Muslim law and religious science- so these future leaders can be well versed in Sharia ⬇
Sharia- the islamic legal code that includes interpretation of the Qur’an and applies islamic principled to daily life
there would even be scholarships
This leads to a very well educated society
They will import paper for education from china and make it better by adding starch to it which will spread to Europe
Tolerance
referring back to the People of the Book
what Muslims called Christians and Jews which means that they too only believe in one god
for the most part tolerant- any persecution of non-muslims is localized and sporadic (not common)
some Jewish people had wealthy and exalted position in society
Rigid moral code= patterns of more growth?
Inter-religious relationships are a thing 😗 and help create the cosmopolitan society
for scholars there is a positive context with this because sharing of ideas and education
Christians, Muslims, and Jews often trade with each other and share art
Status of Women
The society is still a Patriarchy
male dominated society
General improvement in the status of women in Arabia after Islam
Polygamy- multiple wives/ women← Muhammad was a believer of polygamy and had many wives which were held up and exemplified as examples of what a good muslim is
there are places for women in politics
Qur’an implies spiritual equality under Allah for men and women
ex: men are punished the same as women for cases like adultery
not unheard of for women to memorize and recite the Qur’an
However; women also became a form of status in the society with the more women men had the better their status
Veil for women- is not originally seen in the Qur’an- it is a mark of Persian status for upperclass women and a form of modesty
Burqa- the total body covering for women
Harem- translates to “forbidden”; refers to the women’s quarters of the home; symbol of male prestige for men to have a large harem of women to sleep with
Overall the status of women is very fluid
Culture
there will be preservation of classical greek culture by the Islamic empire
europeans largely failed at preserving the greek teachings of Aristotle, Plato, …. because they were pagans
Islamic people had no hang up in reading it and enjoyed a lot of Aristotle’s (and some of Plato’s) teachings
they looked at their teachings as the basis of knowledge and studied their teachings to try to understand how this society had such a strong basis of science→ even wrote commentaries on these original latin and greek texts :0
Science and Medicine→ they learned the concept of zero from India along with the concept of the decimal point» gave rise to Arabic numerals (12345….)
this is where algebra would start to take shape (crap ☹ )
Iba Sina- preeminent physician, compiled greco-roman knowledge on medicine and figured out Tuberculosis is contagious→ studied the spread of disease
was also a philosopher
Bagdad, Persia and other countries in Arabic Peninsula housed the best doctors in the world at this time
development of the hypodermic needles and cauterization
Philosophy
philosophers were expected to find a connection to logic and ones relationship with god
wrote about the ideal ruler based on logic
Sample Questions:
Which of the following did the greeks adapt from the Phoenicians?
the theory of the forms -the prisoners in the cave by Plato
phonetic alphabet
phalanx
Both b and c
Which of the following explains why the greek language and custom were important to the Hellenistic World?
They were common among educated people, which allowed ideas to spread
they provided governmental models
they facilitated trade across a wide geographic expanse
all of the above
Which of the following statements regarding Tiberius Gracchus is true?
He expanded the frontier of Rome into northern Britain
he unsuccessfully attempted to expand the frontier into northern Africa
he struggled to address the economic problems of the plebeians through land reform
all of the above
Which of the following did not contribute to the fall of the Roman Empire?
barbarian invasions
religious factionalism
economic crisis
weakened military
Which of the following does not help explain the strength and endurance of the byzantine empire?
they had no enemies
advantageous city position with water surrounding three sides of it
infrastructure with complex walls and aquifers
very strong army with strong army traditions
Which of the following is the correct definition for the word “Islam”?
“one who submits”
“followers of the prophet”
“submission to god”
“the word of god”
 Knowt
Knowt