
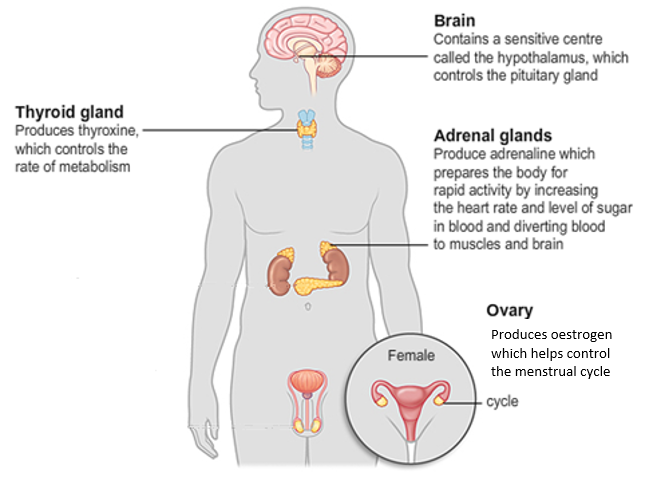
Endocrine System
Hormones- chemical messengers that are made in the endocrine glands.
Endocrine System-Collection of glands taht produce the body’s hormones.
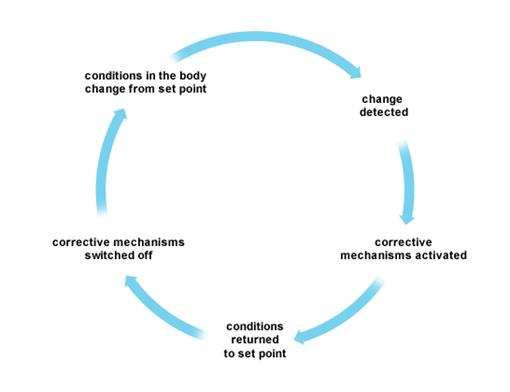
Negative Feedback
Homeostasis- keeping the conditions in your body constant.
Negative Feedback- acts to reverse the original change that occurred. e.g if hormone levels become too high the body will stop producing them, if they become too low, the body will produce them again.
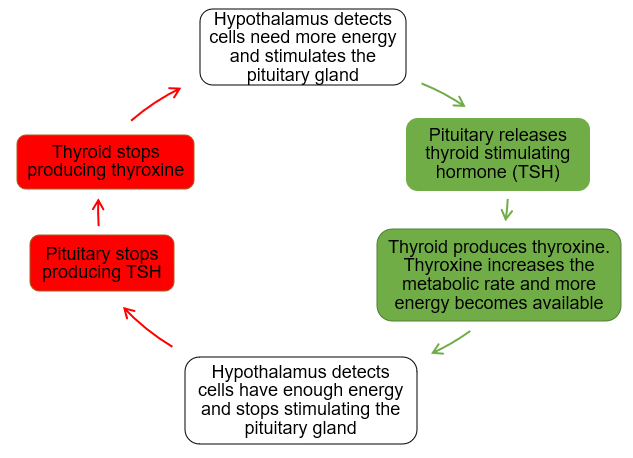
Thyroxine
A hormone produced by the thyroid gland. Controls how much energy is available to the cells by regulating the body’s metabolic rate. Example of negative feedback.
Adrenaline
Hormone produced by the adrenal glands, part of the body’s ‘fight or flight’ response. Adrenaline prepares the body for intense action. This causes the body to respond by:
respiring more quickly, increase the rate of ATP production
increasing the rate of breathing to cope with the extra demand for oxygen
increasing heart rate
diverting blood away from areas e.g. digestive system, towards the muscles.
The menstrual cycle
Main stages of the menstrual cycle:
Menstruation (period) The uterus lining breaks down and along with the unfertilised egg is removed from the body.
Thickening of uterus lining- Each month the uterus thickens in readiness to receive a fertilised egg. At the same time an egg in one of the ovaries will begin to mature.
Ovulation- After the uterus lining begins to thicken, the ovary releases the egg. The lining of the uterus remains thick.
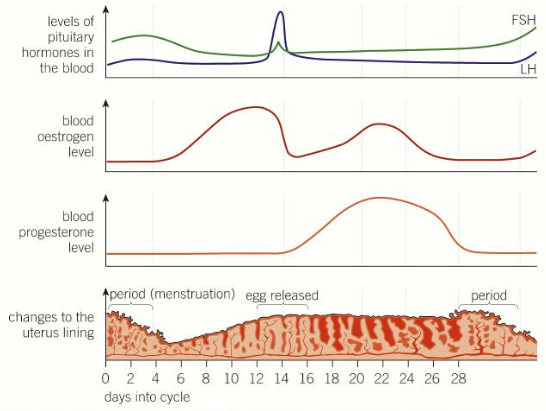
Controlling the menstrual cycle
Controlled by four hormones : Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), Luteinising hormone (LH), oestrogen and progesterone. All made in the pituitary gland and the ovaries.
Follicle-stimulating hormone: FSH is secreted by the pituitary gland before travelling to the ovaries where it causes the egg to mature. FSH stimulates the ovaries to produce oestrogen.
Oestrogen: Produced and secreted by ovaries. Uterus wall thickens up. As oestrogen increases, FSH stops being produced. Prevents more than one egg maturing. Stimulates the pituitary glands to release LH.
LH:
Endocrine System
Hormones- chemical messengers that are made in the endocrine glands.
Endocrine System-Collection of glands taht produce the body’s hormones.

Negative Feedback
Homeostasis- keeping the conditions in your body constant.
Negative Feedback- acts to reverse the original change that occurred. e.g if hormone levels become too high the body will stop producing them, if they become too low, the body will produce them again.

Thyroxine
A hormone produced by the thyroid gland. Controls how much energy is available to the cells by regulating the body’s metabolic rate. Example of negative feedback.

Adrenaline
Hormone produced by the adrenal glands, part of the body’s ‘fight or flight’ response. Adrenaline prepares the body for intense action. This causes the body to respond by:
respiring more quickly, increase the rate of ATP production
increasing the rate of breathing to cope with the extra demand for oxygen
increasing heart rate
diverting blood away from areas e.g. digestive system, towards the muscles.
The menstrual cycle
Main stages of the menstrual cycle:
Menstruation (period) The uterus lining breaks down and along with the unfertilised egg is removed from the body.
Thickening of uterus lining- Each month the uterus thickens in readiness to receive a fertilised egg. At the same time an egg in one of the ovaries will begin to mature.
Ovulation- After the uterus lining begins to thicken, the ovary releases the egg. The lining of the uterus remains thick.
Controlling the menstrual cycle
Controlled by four hormones : Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), Luteinising hormone (LH), oestrogen and progesterone. All made in the pituitary gland and the ovaries.
Follicle-stimulating hormone: FSH is secreted by the pituitary gland before travelling to the ovaries where it causes the egg to mature. FSH stimulates the ovaries to produce oestrogen.
Oestrogen: Produced and secreted by ovaries. Uterus wall thickens up. As oestrogen increases, FSH stops being produced. Prevents more than one egg maturing. Stimulates the pituitary glands to release LH.
LH:

 Knowt
Knowt