
6.2 State Expansion
Essential Question: By what processes did state powershift in various parts of the world between 1750 and 1900?
Art/Technology:
-In the 1800s, quinine was discovered, a medicine that treats the tropical disease malaria, reducing the danger of living in warm, humid regions.
-Many European nations dreamed of dramatically shortening the water route to Asia by building a canal connecting the Red Sea with the Mediterranean Sea. The 100 mile long canal would save a trip around the entire continent of Africa. This was accomplished in 1869 with the development of the Suez canal. Work was performed by 1.5 million Egyptians known as carvee laborers, unpaid workers who were forced as a form of taxation.
Social:
-In the Cape Colony, Britain introduced the use of English but allowed people to use the Dutch language as well.
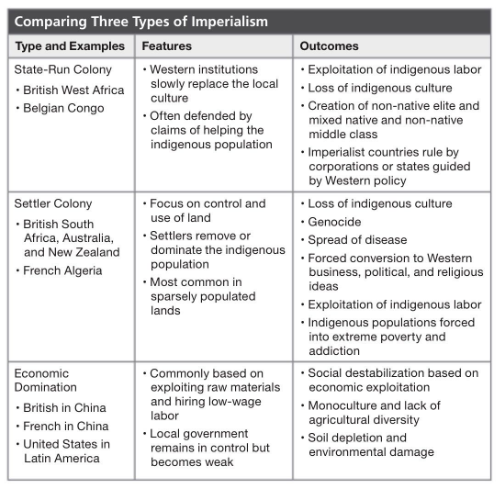
-In Congo under the control of Leopold, the labor conditions were brutal. Leopold’s agents would sever the hands of Congolese workers to terrorize the others into submission. Workers who didn’t meet their quotas were beaten and killed, while others were worked to death. Sometimes spouses were held captive so the workers would not run away.
-Adding to China’s internal problems, the Yellow River (Huang He) changed course, flooding farmland in some areas and leaving others open to drought. WIth agricultural lands devastated, famine followed during which many Chinese starved to death. The Bubonic plague was spreading at the same time.
Political:
-The Dutch government revoked the charter of the Dutch East India Company for abusing its power to make treaties, build forts, and maintain armed forces in Southeast Asia.
-The French seized Algeria in 1830 from the Ottomans, declaring they wanted to prevent pirate attacks. By 1870, it had become a settler colony.
-In the second half of the 1800s, European nations expanded their presence in Africa with the help of better military technology.
-When unrest in Egypt threatened British commercial interests and the operation of the canal in 1882, Britain seized control of Egypt away from the Ottoman Empire.
British West Africa:
Sierra Leone was established in 1787 and was a home for freed people from the British Empire who has been enslaved.
Gambia was established in 1816. Along with Sierra Leone, it was used as a base to stop the exportation of enslaved people.
Lagos became a crown colony in 1861 and served as a base for the annexation of much of the rest of what is now Nigeria.
Britain acquired what is now Ghana in stages. The Gold Coast became a crown colony in 1874, but the Asante Empire didn’t come under British control until 1901.
-In 1873, Britain signed a treaty with King Jaja of Opobo in present day Nigeria- an area rich in palm oil- recognizing him as ruler and agreeing to trade terms favorable to both sides. Other African rulers agreed to similar treaties, but as competition increased and warfare broke out, these treaties became meaningless.
-Otto von Bismarck of Germany had little interest in colonies, but he did want to keep the peace in Europe. In 1884-1885, he hosted the Berlin Conference, a meeting of European powers to provide for the orderly colonization of Africa. Africans were not invited to the conference. An agreement about colonial lines and free movement of goods was acheived.
-During the Napoleonic Wars (1799-1815), the British replaced the Dutch in the Cape Colony in the southern tip of Africa.
-Many of the Dutch-speaking Afrikaners, the descendants of the 17th-century Dutch settlers, moved east of the Cape Colony, where they came into conflict with indigenous groups, including the Zulus, with whom they fought several wars.
-The Boer Wars (1880-1881, 1899-1902)
Conflicts were bloody and brutal
British army drove the Afrikaners and the Africans from their lands, forcing many into refugee camps.
These camps were seperated by race and known as concentration camps.
Medical care and sanitation were very poor, and food rations were extremely meager.
When news of this arrived in Britain, activists attempted to improve the lives of displaced refugees.
White camps received some attention, where black camps remained terrible.
Of the 100,000 black people interned in concentration camps, nearly 15,000 perished.
-King Leopold II of Belgium (ruled 1865-1909) oversaw the invasion and pacification of the Congo in central Africa in order to persuade the Belgian government to support colonial expansion. Unlike other European rulers, King Leopold owned the colony personally, using colonial officials against indigenous Congolese and a ruthless system of economic exploitation that allowed him to keep the profits made by the Congo Free State, which totaled some 220 million francs ($1.1 billion in today’s dollars).
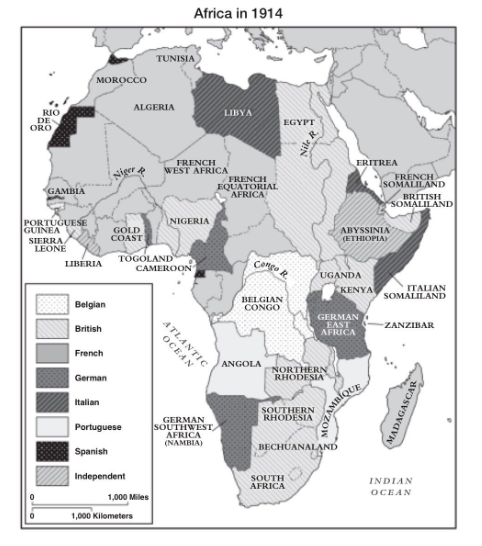
-By 1900, the only African countries unclaimed by Europeans were Abyssinia (modern-day Ethiopia) and Liberia, a country founded by formerly enslaved people from the United States.
-Italy attempted to conquer Abyssinia in 1895, but the natives were to strong for the Italians.
-Portugal, France, and England competed for control of India’s spices, gems, and trade with regions to the east.
-China maintained its own government throughout a period of European economic domination. As a result of military strength, European nations carved out spheres of influence within China over which they had exclusive trading rights and access to natural resources.
-Internal problems within the Qing government, like the Taiping Rebellion, made it easier for foreign countries to dominate the economic affairs of China.
During the Taiping Rebellion, which began in 1850, failed civil servant applicant Hong Xiuquan and starving peasants, workers, and miners attempted to overthrow the Qing Dynasty. With the use of French and British intervention, the Qing Dynasty prevailed in 1864.
Intellectual:
Religious:
-Between 1899 and 1901, an anti-imperialist group called the Boxers- named because many of their members practiced martial arts, which were known as Chinese boxing- was attacking Chinese Christians and Western missionaries.
Economic:
-Although most European countries had declared the importation of slaves from Africa illegal by the early 1800s, Europeans continued to export guns, alcohol, and other manufactured goods to Africa and import African natural resources, such as palm oil, gold, and ivory. England desired palm oil in particular because it kept the machinery in its textile factories from becoming rusty.
6.2 State Expansion
Essential Question: By what processes did state powershift in various parts of the world between 1750 and 1900?
Art/Technology:
-In the 1800s, quinine was discovered, a medicine that treats the tropical disease malaria, reducing the danger of living in warm, humid regions.
-Many European nations dreamed of dramatically shortening the water route to Asia by building a canal connecting the Red Sea with the Mediterranean Sea. The 100 mile long canal would save a trip around the entire continent of Africa. This was accomplished in 1869 with the development of the Suez canal. Work was performed by 1.5 million Egyptians known as carvee laborers, unpaid workers who were forced as a form of taxation.
Social:
-In the Cape Colony, Britain introduced the use of English but allowed people to use the Dutch language as well.
-In Congo under the control of Leopold, the labor conditions were brutal. Leopold’s agents would sever the hands of Congolese workers to terrorize the others into submission. Workers who didn’t meet their quotas were beaten and killed, while others were worked to death. Sometimes spouses were held captive so the workers would not run away.
-Adding to China’s internal problems, the Yellow River (Huang He) changed course, flooding farmland in some areas and leaving others open to drought. WIth agricultural lands devastated, famine followed during which many Chinese starved to death. The Bubonic plague was spreading at the same time.
Political:
-The Dutch government revoked the charter of the Dutch East India Company for abusing its power to make treaties, build forts, and maintain armed forces in Southeast Asia.
-The French seized Algeria in 1830 from the Ottomans, declaring they wanted to prevent pirate attacks. By 1870, it had become a settler colony.
-In the second half of the 1800s, European nations expanded their presence in Africa with the help of better military technology.
-When unrest in Egypt threatened British commercial interests and the operation of the canal in 1882, Britain seized control of Egypt away from the Ottoman Empire.
British West Africa:
Sierra Leone was established in 1787 and was a home for freed people from the British Empire who has been enslaved.
Gambia was established in 1816. Along with Sierra Leone, it was used as a base to stop the exportation of enslaved people.
Lagos became a crown colony in 1861 and served as a base for the annexation of much of the rest of what is now Nigeria.
Britain acquired what is now Ghana in stages. The Gold Coast became a crown colony in 1874, but the Asante Empire didn’t come under British control until 1901.
-In 1873, Britain signed a treaty with King Jaja of Opobo in present day Nigeria- an area rich in palm oil- recognizing him as ruler and agreeing to trade terms favorable to both sides. Other African rulers agreed to similar treaties, but as competition increased and warfare broke out, these treaties became meaningless.
-Otto von Bismarck of Germany had little interest in colonies, but he did want to keep the peace in Europe. In 1884-1885, he hosted the Berlin Conference, a meeting of European powers to provide for the orderly colonization of Africa. Africans were not invited to the conference. An agreement about colonial lines and free movement of goods was acheived.
-During the Napoleonic Wars (1799-1815), the British replaced the Dutch in the Cape Colony in the southern tip of Africa.
-Many of the Dutch-speaking Afrikaners, the descendants of the 17th-century Dutch settlers, moved east of the Cape Colony, where they came into conflict with indigenous groups, including the Zulus, with whom they fought several wars.
-The Boer Wars (1880-1881, 1899-1902)
Conflicts were bloody and brutal
British army drove the Afrikaners and the Africans from their lands, forcing many into refugee camps.
These camps were seperated by race and known as concentration camps.
Medical care and sanitation were very poor, and food rations were extremely meager.
When news of this arrived in Britain, activists attempted to improve the lives of displaced refugees.
White camps received some attention, where black camps remained terrible.
Of the 100,000 black people interned in concentration camps, nearly 15,000 perished.
-King Leopold II of Belgium (ruled 1865-1909) oversaw the invasion and pacification of the Congo in central Africa in order to persuade the Belgian government to support colonial expansion. Unlike other European rulers, King Leopold owned the colony personally, using colonial officials against indigenous Congolese and a ruthless system of economic exploitation that allowed him to keep the profits made by the Congo Free State, which totaled some 220 million francs ($1.1 billion in today’s dollars).

-By 1900, the only African countries unclaimed by Europeans were Abyssinia (modern-day Ethiopia) and Liberia, a country founded by formerly enslaved people from the United States.
-Italy attempted to conquer Abyssinia in 1895, but the natives were to strong for the Italians.
-Portugal, France, and England competed for control of India’s spices, gems, and trade with regions to the east.
-China maintained its own government throughout a period of European economic domination. As a result of military strength, European nations carved out spheres of influence within China over which they had exclusive trading rights and access to natural resources.
-Internal problems within the Qing government, like the Taiping Rebellion, made it easier for foreign countries to dominate the economic affairs of China.
During the Taiping Rebellion, which began in 1850, failed civil servant applicant Hong Xiuquan and starving peasants, workers, and miners attempted to overthrow the Qing Dynasty. With the use of French and British intervention, the Qing Dynasty prevailed in 1864.

Intellectual:
Religious:
-Between 1899 and 1901, an anti-imperialist group called the Boxers- named because many of their members practiced martial arts, which were known as Chinese boxing- was attacking Chinese Christians and Western missionaries.
Economic:
-Although most European countries had declared the importation of slaves from Africa illegal by the early 1800s, Europeans continued to export guns, alcohol, and other manufactured goods to Africa and import African natural resources, such as palm oil, gold, and ivory. England desired palm oil in particular because it kept the machinery in its textile factories from becoming rusty.
 Knowt
Knowt