
Science 4th
Digestive system Pt1.
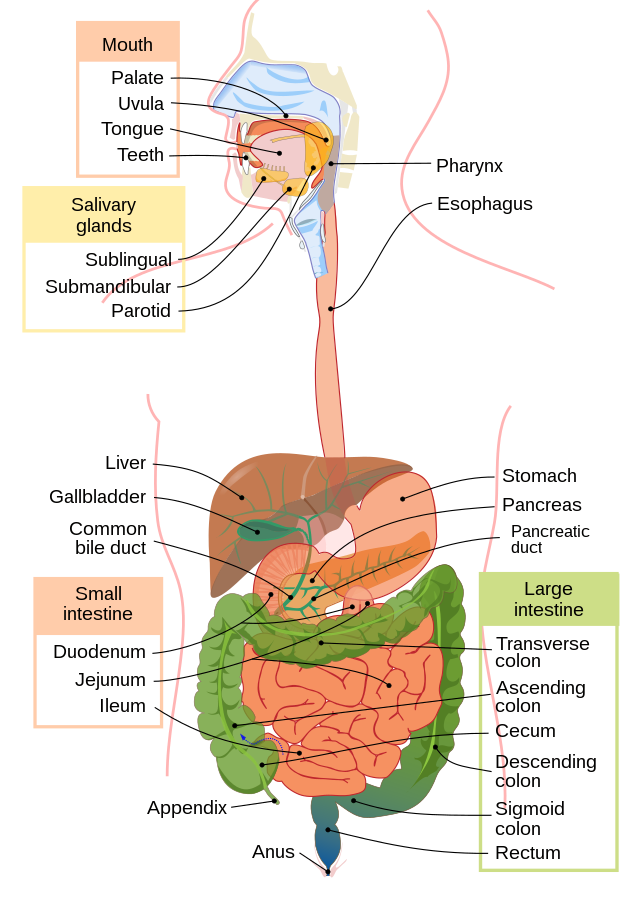
Digestive system - Responsible for the digestion and absorption of foods
THE SIX TYPES OF NUTRIENS OUR BODY NEEDS
Nutrients
Lipids(FATS)
Vitamins
Minerals
Carbohydrates
Proteins
Water
Food is a nourishing substance that we take into our body through eating or drinking
Metabolism -is the process of how the cells use the energy that they obtain from food during digestion.
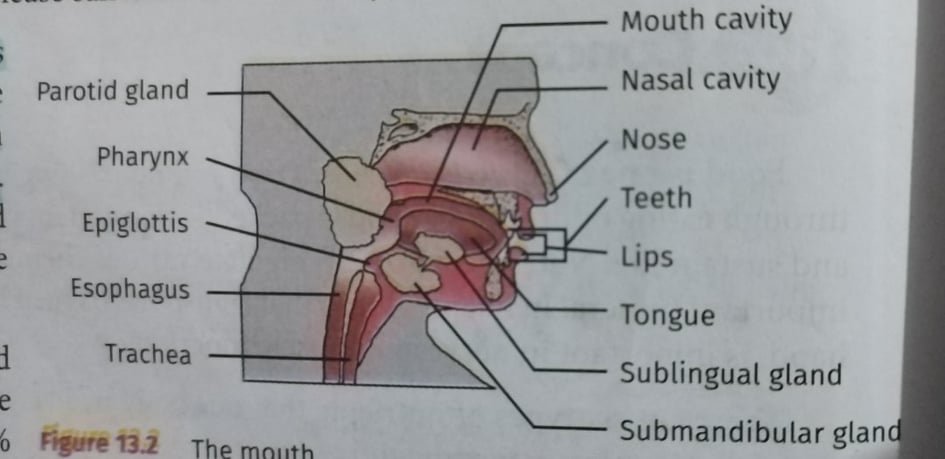
Digestive Tube or Alimentary Canal - Where the food is digested
Mouth or Oral cavity - The entry point of the food
Ingestion - The FIRST STAGE of digestion
- Begins with MASTICATION or CHEWING
THE THREE MAJOR SALIVARY GLANDS
Parotid
Sublingual
Submandibular
Parotid glands - are located on the side of the cheeks
Submandibular glands - are located beneath the lower jaw
Sublingual glands - are the glands that are situated under the tongue
Exocrine glands or glands - produce or secrete substances that protect or lubricate a certain body part
There are about 800 - 1000 minor salivary glands Such as:
Labial
Buccal
Glossopalatine
Palatine
Lingual glands
Saliva contains an ENZYME called Ptyalin or Salivary amylase
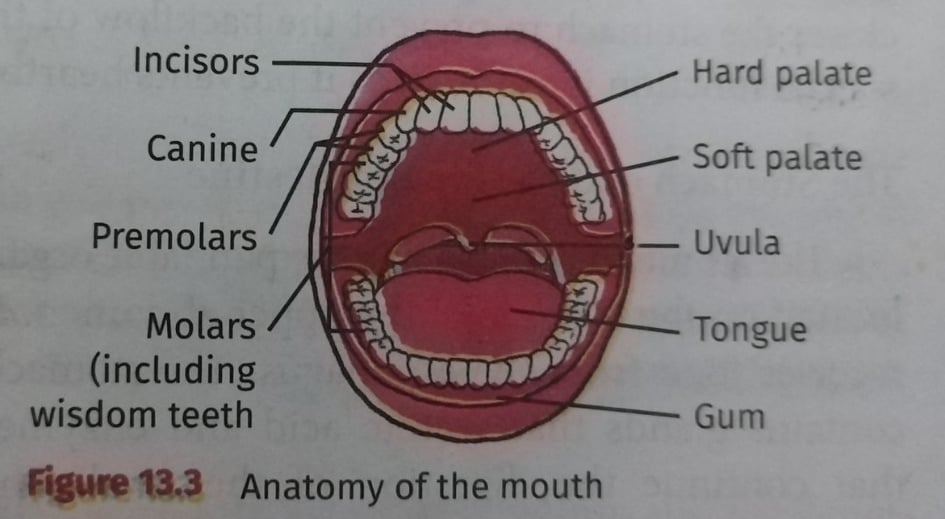
INCISORS and CANINE - used for tearing or biting food
PREMOLARS and MOLARS - ideal for chewing
Adults usually have 32 TEETH
Children mostly have 20 PRIMARY TEETH
Soft palate - the tongue and roof of the mouth
- helps push the food down to the pharynx and esophagus
Papillae - the rough surface of the tongue
Capsaicin - the taste buds that detect spice because of its component
- is a compound found in most numbers of the chili pepper family
Taste receptors - helps detect different taste buds
THE PHARYNX AND THE ESOPHAGUS
Pharynx or throat - it connects to the mouth to the esophagus
- it serves as the passageway for both food and air
Windpipe - is another tube that is also connected to pharynx
Epiglottis - is a pharynx flap
Bolus - is the rounded soft mass of chewed food
ESOPHAGUS - is a muscular tube that is approximately 25 cm long
Peristalsis - is the series of involuntary, wavelike muscular contractions that usually occur in the digestive tract
LOWER ESOPHAGEAL SPINCHTER %%(LES) called muscular valve - relaxes and allows food to pass into stomach
Stomach -is a muscular, expanded organ located on the left side of the upper abdomen. receive the food from esophagus
GASTRIC JUICE - is composed of Hydrochloric acid (HCI) and digestive enzyme called pepsin
Science 4th
Digestive system Pt1.

Digestive system - Responsible for the digestion and absorption of foods
THE SIX TYPES OF NUTRIENS OUR BODY NEEDS
Nutrients
Lipids(FATS)
Vitamins
Minerals
Carbohydrates
Proteins
Water
Food is a nourishing substance that we take into our body through eating or drinking
Metabolism -is the process of how the cells use the energy that they obtain from food during digestion.

Digestive Tube or Alimentary Canal - Where the food is digested
Mouth or Oral cavity - The entry point of the food
Ingestion - The FIRST STAGE of digestion
- Begins with MASTICATION or CHEWING
THE THREE MAJOR SALIVARY GLANDS
Parotid
Sublingual
Submandibular
Parotid glands - are located on the side of the cheeks
Submandibular glands - are located beneath the lower jaw
Sublingual glands - are the glands that are situated under the tongue
Exocrine glands or glands - produce or secrete substances that protect or lubricate a certain body part
There are about 800 - 1000 minor salivary glands Such as:
Labial
Buccal
Glossopalatine
Palatine
Lingual glands
Saliva contains an ENZYME called Ptyalin or Salivary amylase

INCISORS and CANINE - used for tearing or biting food
PREMOLARS and MOLARS - ideal for chewing
Adults usually have 32 TEETH
Children mostly have 20 PRIMARY TEETH
Soft palate - the tongue and roof of the mouth
- helps push the food down to the pharynx and esophagus
Papillae - the rough surface of the tongue
Capsaicin - the taste buds that detect spice because of its component
- is a compound found in most numbers of the chili pepper family
Taste receptors - helps detect different taste buds
THE PHARYNX AND THE ESOPHAGUS
Pharynx or throat - it connects to the mouth to the esophagus
- it serves as the passageway for both food and air
Windpipe - is another tube that is also connected to pharynx
Epiglottis - is a pharynx flap
Bolus - is the rounded soft mass of chewed food
ESOPHAGUS - is a muscular tube that is approximately 25 cm long
Peristalsis - is the series of involuntary, wavelike muscular contractions that usually occur in the digestive tract
LOWER ESOPHAGEAL SPINCHTER %%(LES) called muscular valve - relaxes and allows food to pass into stomach
Stomach -is a muscular, expanded organ located on the left side of the upper abdomen. receive the food from esophagus
GASTRIC JUICE - is composed of Hydrochloric acid (HCI) and digestive enzyme called pepsin
 Knowt
Knowt