
Reflection
All waves can be absorbed, transmitted or reflected
When waves arrive at a boundary between two different materials, three things can happen:
The waves are absorbed by the material the wave is trying to cross into-this transfers energy to the material’s energy stores
The waves are transmitted-the waves carry on travelling through the new material, which often leads to refraction
The waves are reflected
What actually happens depends on the wavelength of the wave and the properties if the materials involved
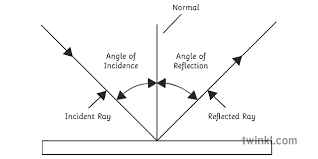
You can draw a simple ray diagram for reflection
There’s one simple rule to learn for all reflected waves:
Angle of incidence = Angle of reflection
The angle of incidence is the angle between the incoming wave and normal
The angle of reflection is the angle between the reflected wave and the normal
The normal is an imaginary line that’s perpendicular to the surface at the point of incidence
The normal is usually shown as a dotted line
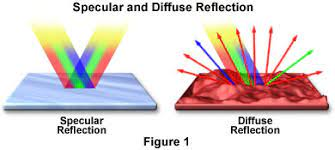
Reflection can be specular or diffuse
Waves are reflected at different boundaries in different ways
Specular reflection happens when a wave is reflected in a single direction by a smooth surface
Diffuse reflection us when a wave is reflected by a rough surface and the reflected rays are scattered in lots of different directions
This happens because the normal is different for each incoming ray, which means that the angle of incidence for each ray. The rule of angle of incidence = angle of reflection still applies
When light is reflected by a rough surface, the surface appears matte and you don’t get a clear refection of objects
Reflection
All waves can be absorbed, transmitted or reflected
When waves arrive at a boundary between two different materials, three things can happen:
The waves are absorbed by the material the wave is trying to cross into-this transfers energy to the material’s energy stores
The waves are transmitted-the waves carry on travelling through the new material, which often leads to refraction
The waves are reflected
What actually happens depends on the wavelength of the wave and the properties if the materials involved
You can draw a simple ray diagram for reflection
There’s one simple rule to learn for all reflected waves:
Angle of incidence = Angle of reflection
The angle of incidence is the angle between the incoming wave and normal
The angle of reflection is the angle between the reflected wave and the normal
The normal is an imaginary line that’s perpendicular to the surface at the point of incidence
The normal is usually shown as a dotted line

Reflection can be specular or diffuse
Waves are reflected at different boundaries in different ways
Specular reflection happens when a wave is reflected in a single direction by a smooth surface
Diffuse reflection us when a wave is reflected by a rough surface and the reflected rays are scattered in lots of different directions
This happens because the normal is different for each incoming ray, which means that the angle of incidence for each ray. The rule of angle of incidence = angle of reflection still applies
When light is reflected by a rough surface, the surface appears matte and you don’t get a clear refection of objects

 Knowt
Knowt