
AP BIOLOGY Review
AMINO ACIDS
there are 20 amino acids
Our proteins are made of some of these combinations of these amino acids
there are 4 levels of protein structure
primary - the order of the amino acids in that chain (string)
secondary - helix - alpha helix - beta pleated sheets (coils and sheets)
tertiary - an individual polypeptide
quaternary - made up of 4 polypeptides (Transthyretin) two alpha subunits and two beta subunits
bonds between amino acids are peptide bonds - formed by a dehydration reaction - a water molecule is produced from that action
hydrogen bond
Di-sulfide bridge - firm covalent bond
Van Der Waals interactions (no need to explain it)
ionic bond
hydrophobic interaction is when things that are hydrophobic are pushed together (in oil in water)
4 atoms of iron for one Hemoglobin molecule
SUGAR-PHOSPHATE BACKBONE
Sugars have carbons on unlabeled corners
they can have a number of carbons but the most common are glucose and fructose (six carbons)
phosphate ground has 4 oxygens one double bond and the central atom is a phosphate
sugars have a phosphate group, a sugar, and a nitrogenous base
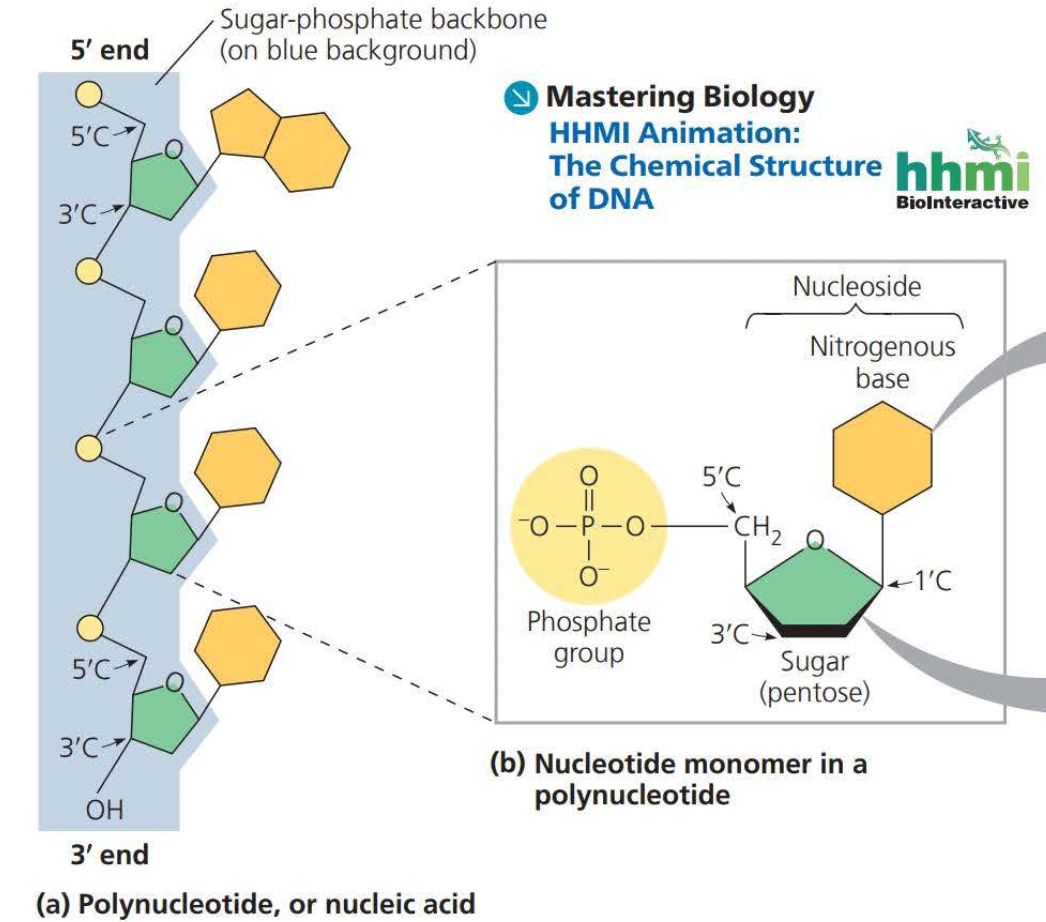
The picture represents an RNA because its a singular strand and not a double strand 5’ and 3’ are opposites so in DNA one will be 5’ and the other will be 3’
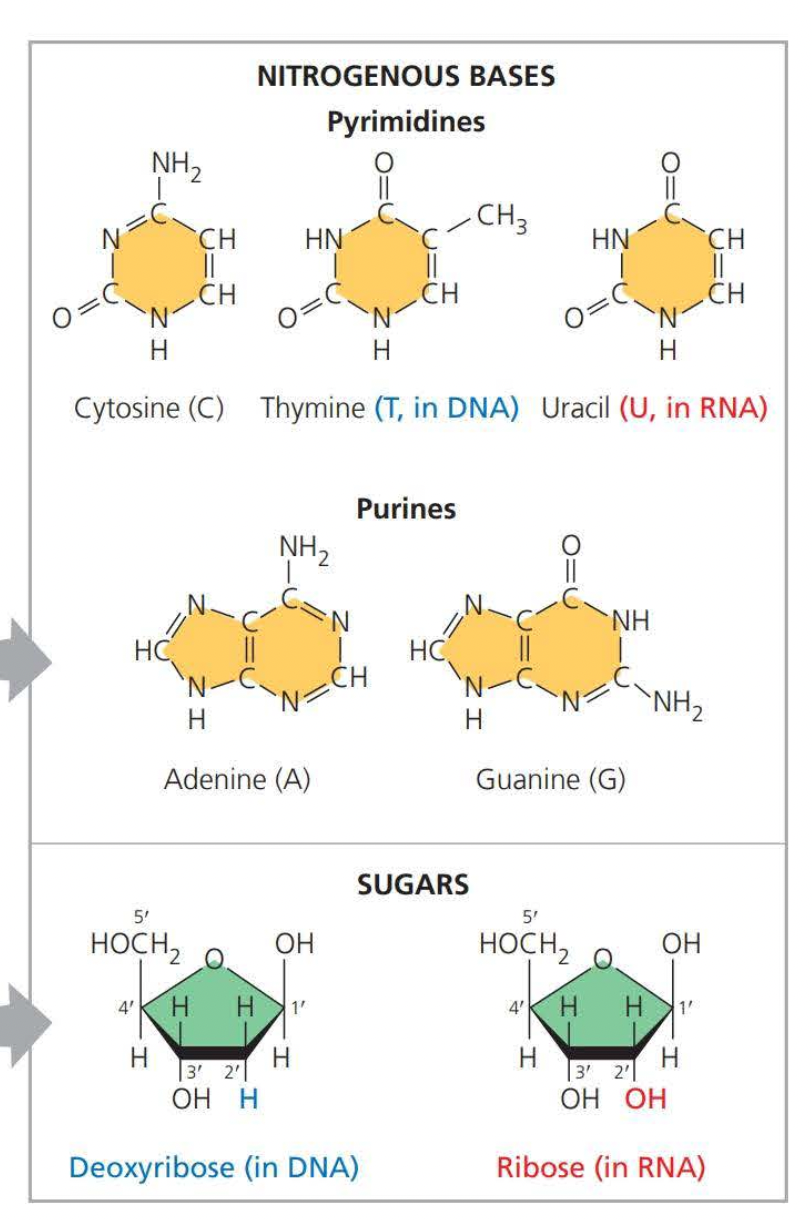
Need to know that pyrimidines are singular rings
And purines are double rings
RNA may fold on itself but will still be a single strand
RNA components
Adenine
Cytosine
Thymine
Uracil
DNA components
Adenine
Cytosine
Thymine
Guanine
Adenine - Thymine
Cytosine - Guanine
or
Cytosine - Uracil
Diagram of an RNA folding over on itself

CHECK THE CHAPTER REVIEWS IN CAMPBELL’S BIOLOGY IN FOCUS
AP BIOLOGY Review
AMINO ACIDS
there are 20 amino acids
Our proteins are made of some of these combinations of these amino acids
there are 4 levels of protein structure
primary - the order of the amino acids in that chain (string)
secondary - helix - alpha helix - beta pleated sheets (coils and sheets)
tertiary - an individual polypeptide
quaternary - made up of 4 polypeptides (Transthyretin) two alpha subunits and two beta subunits
bonds between amino acids are peptide bonds - formed by a dehydration reaction - a water molecule is produced from that action
hydrogen bond
Di-sulfide bridge - firm covalent bond
Van Der Waals interactions (no need to explain it)
ionic bond
hydrophobic interaction is when things that are hydrophobic are pushed together (in oil in water)
4 atoms of iron for one Hemoglobin molecule
SUGAR-PHOSPHATE BACKBONE
Sugars have carbons on unlabeled corners
they can have a number of carbons but the most common are glucose and fructose (six carbons)
phosphate ground has 4 oxygens one double bond and the central atom is a phosphate
sugars have a phosphate group, a sugar, and a nitrogenous base

The picture represents an RNA because its a singular strand and not a double strand 5’ and 3’ are opposites so in DNA one will be 5’ and the other will be 3’
Need to know that pyrimidines are singular rings
And purines are double rings

RNA may fold on itself but will still be a single strand
RNA components
Adenine
Cytosine
Thymine
Uracil
DNA components
Adenine
Cytosine
Thymine
Guanine
Adenine - Thymine
Cytosine - Guanine
or
Cytosine - Uracil
Diagram of an RNA folding over on itself

CHECK THE CHAPTER REVIEWS IN CAMPBELL’S BIOLOGY IN FOCUS
 Knowt
Knowt
